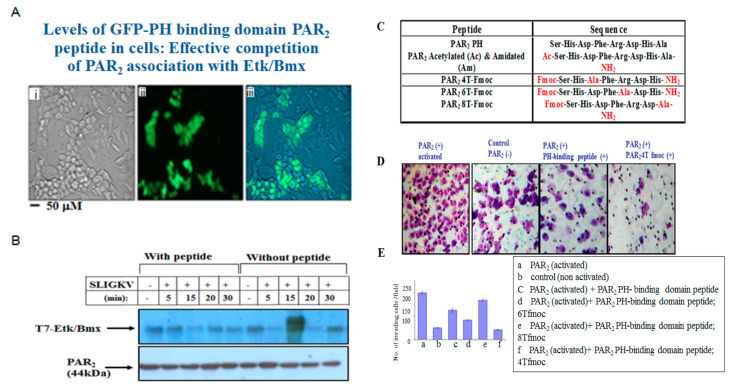
Figure 5.
Characterization of PAR2-PH binding domain peptides. (A) GFP-PH binding domain peptide penetration to HEK293 cells (ii,iii) as compared to untreated cells (i). (B) Potent inhibition of the PAR2-Etk/Bmx association by the GFP-PAR2-PH binding domain peptide. HEK 293 cells transfected with Par2/f2rl1. Immunoprecipitation of cell lysates in the presence and absence of the peptide was performed, following SLIGKV activation for various time periods. Etk/Bmx was detected by anti-T7 abs. Levels of PAR2 immunoprecipitate were detected by anti-PAR2 abs. (C) Table showing the list of PAR2-PH binding domain peptides (wt and modified peptides). (D) Matrigel invasion in the presence and absence of PAR2 SLIGKV activation. Representative modified peptides are shown. (E) Histograms of the wt and various modified PAR2-PH binding domain peptides in the Matrigel invasion assay.