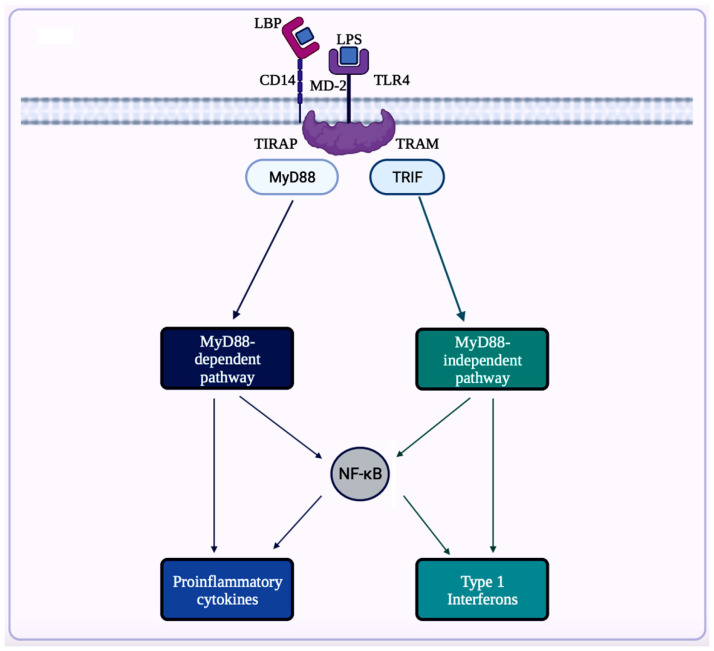
Figure 4.
This illustration showcases an overview of LPS/TLR4 signaling. LPS can attach to LPS binding protein (LBP), which assists the transfer of LPS to glycerophosphatidylinositol-anchored protein (CD14). Then, CD14 transfers LPS to the TLR4/myeloid differentiation factor-2 (MD-2) receptor complex. After recognizing LPS, this complex triggers signals via toll-interleukin 1-receptor domain-containing adaptor protein (TIRAP) and myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88) for activation of NF-κB to induce expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines. The LPS/TLR4 signaling can also be mediated via TRIF-related adaptor molecule (TRAM) and TIR domain-containing adaptor protein-inducing interferon-β (TRIF) in the MyD88-independent pathway. These adaptor molecules (TRAM and TRIF) activate the transcription factor, interferon regulatory factor-3 (IRF3), to produce type 1 interferons. This figure was created with BioRender.com.