Figure 9.
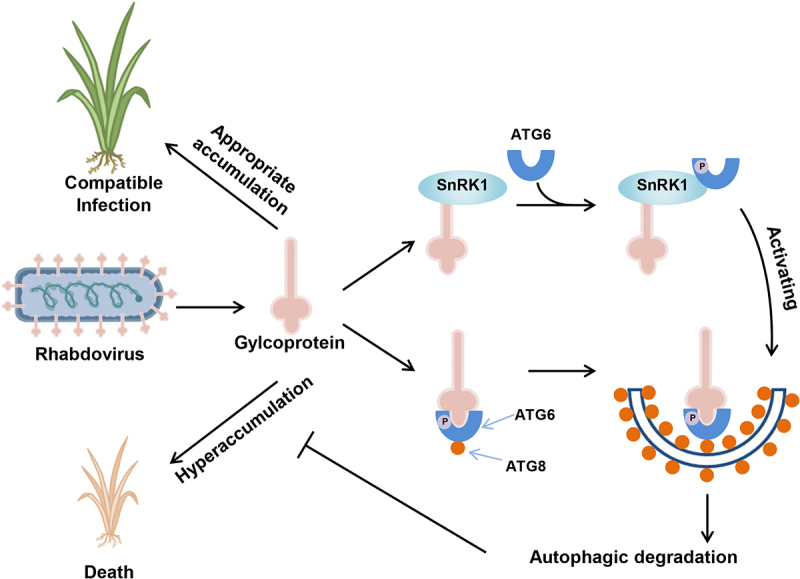
A proposed model illustrates how rhabdovirus encoded glycoprotein induces and harnesses host antiviral autophagy for maintaining its compatible infection. RSMV-encoded glycoprotein triggers host autophagy by interacting with OsSnRK1B and promotes its kinase activity on ATG6, and the glycoprotein can be recognized by ATG6, which serves as a bridge to link glycoproteins to key autophagosome protein ATG8 for degradation. The induction of autophagy functions as an antiviral mechanism against RSMV in rice plants. Moreover, the hyperaccumulation of RSMV glycoprotein is toxic for plant cells, so its targeted degradation by autophagy was essential to restrict the viral titer in plants.
