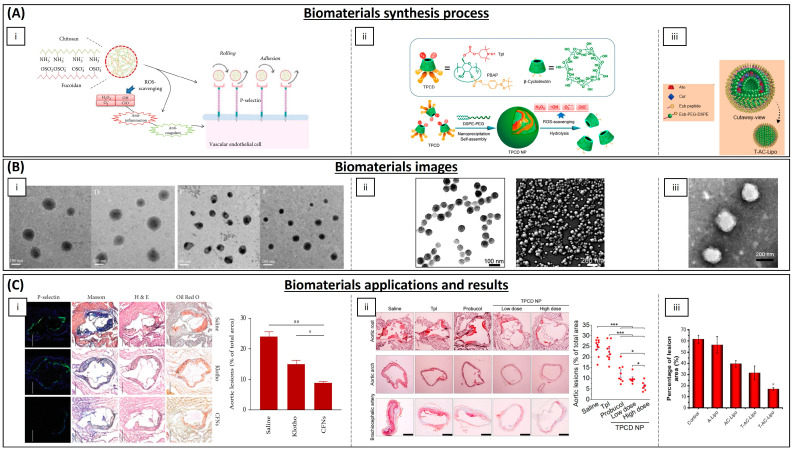
Figure 7.
Some biomaterials currently used for the treatment of atherosclerosis. (A) Synthesis process of the biomaterials. (i) Illustration of the synthesis of CFNs with P-selectin targeting potential, to block leukocyte recruitment and rolling on platelets and endothelium in atherosclerotic plaques [185]. (ii) Chemical structure of a broad-spectrum ROS-scavenging material TPCD and development of a TPCD NP [186]. (iii) Illustration of E-selectin-targeting liposomes (T-AC-Lipo), simultaneously encapsulating atorvastatin calcium (Ato) and Cur [181]. (B) Biomaterials images. (i) TEM image of CNFs (scale bars: (left) 100 nm; (right) 200 nm) [185]. (ii) TEM (left) and SEM (right) images of TPCD NPs [186]. (iii) TEM image of T-AC-Lipo [181]. (C) Results of the biomaterials as treatments of neurodegenerative diseases. (i) These results show that targeted P-selectin delivery by CFNs strikingly attenuates atherosclerotic development and stabilizes the atherosclerotic plaques. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01 [185]. (ii) Observation on ORO-stained cryosections from the aortic sinus, aortic arch and brachiocephalic artery revealed the most significant antiatherosclerotic activity for TPCD NPs at both low and high doses. The quantitative analysis of the lesion area in aortas show that it was notably reduced after therapy with TPCD NPs. * p < 0.05; *** p < 0.001 [186]. (iii) Results indicate that the treatment with T-AC-Lipo resulted in a decrease in the lesion area in aortas [181]. * p < 0.05. All images reproduced with permission. Images (A(i),B(i),C(i)) [185] 2022, Mingying Liu et al. Images (A(ii),B(ii),C(ii)) [186] 2018, American Chemical Society. Images (A(iii),B(iii),C(iii)) [181] 2019, Li X et al.