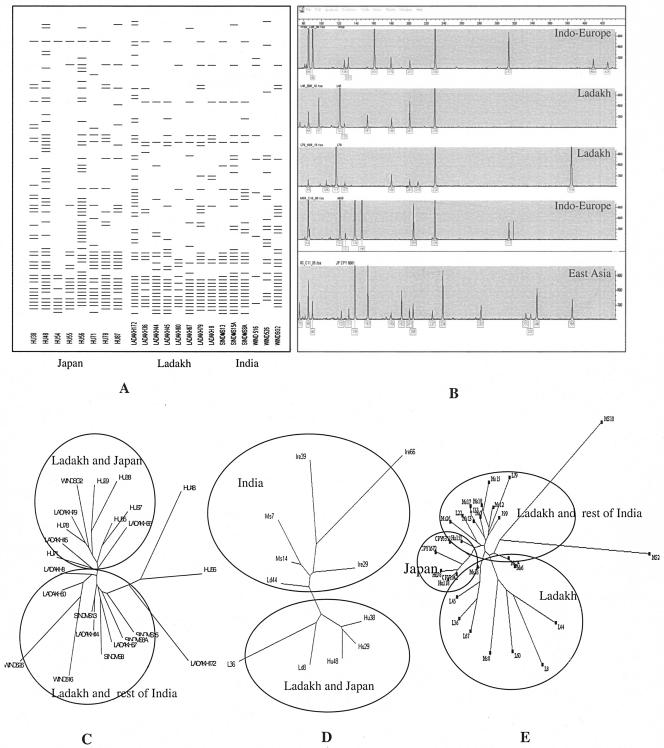
FIG. 2.
Genomic diversity of H. pylori from Ladakh as revealed by FAFLP-based genotyping (A, B, and C) and polymorphisms within the glmM and babB genes. Part A corresponds to the two-dimensional gel image depicting the number of polymorphic loci that were compared before genetic affinities among Ladakhi, Indian, and Japanese strains were deduced in the form of a phylogenetic tree (C). The Genotyper plot (B) corresponding to FAFLP analysis was developed by the Genescan and Genotyper software (Applied Biosystems). It compares FAFLP allelic profiles of Ladakhi strains with Indo-European and East Asian gene pools. Phylogenetic trees were also deduced based on DNA sequence divergence analyses corresponding to glmM (D) and babB (E) genes.