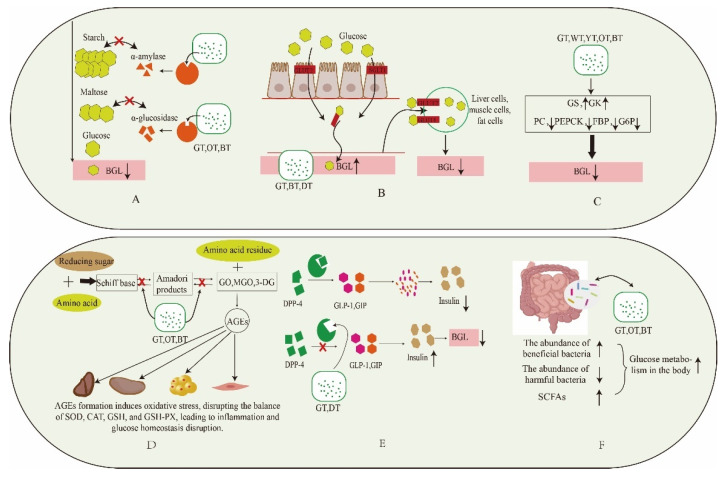
Figure 3.
Mechanism of different fermentation degree tea in balancing postprandial blood glucose. (A): Inhibition of digestive enzymes. (B): Effect on glucose transport. (C): Inhibition of gluconeogenesis pathway. (D): Inhibition of formation of AGEs. (E): Inhibition of DPP-4 activity. (F): Regulation of gut microbiota. Blood glucose levels (BGL); glucokinase (GK); glycogen synthase kinase (GSK); pyruvate carboxylase (PC); phosphoenolpyruvate carboxy kinase (PEPCK); gructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (FBP); glucose-6-phosphatase (G6P); glyoxal (GO), methylglyoxal (MGO),3-meoxyglucosone (3-DG); superoxide dismutase (SOD); catalase (CAT); glutathione (GSH); glutathione peroxidase (GSH-PX). Downward arrow means down-regulation. Upward arrow means up-regulation.