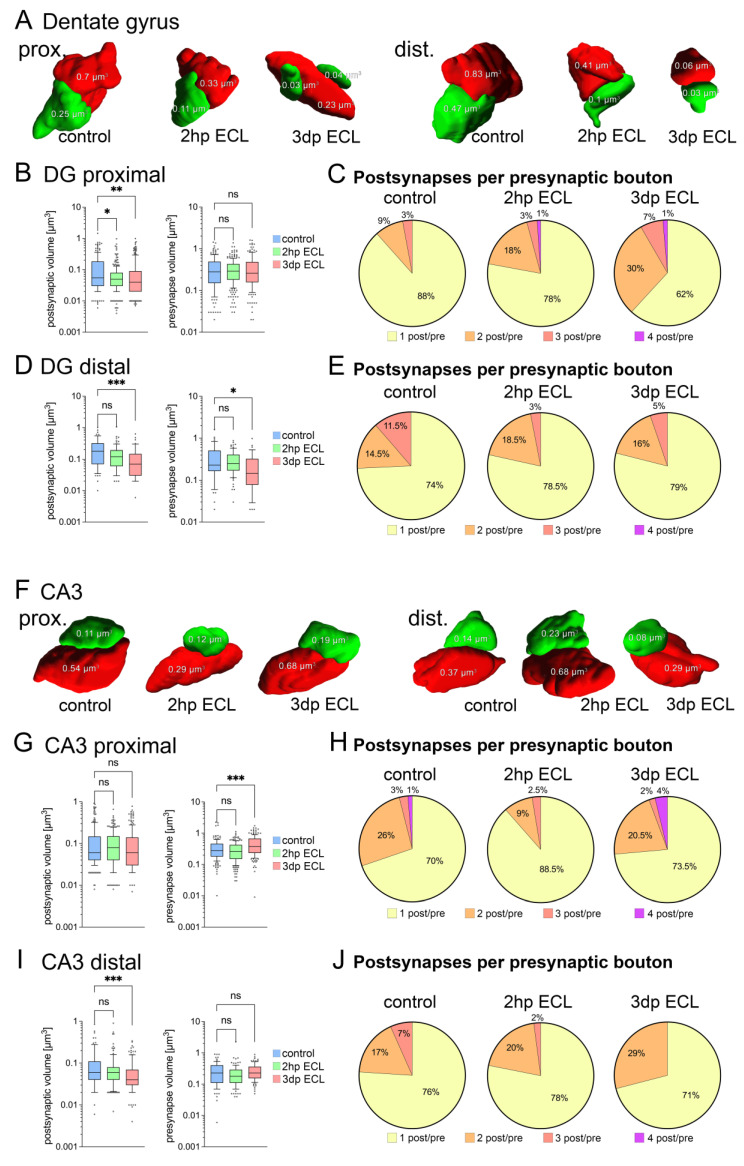
Figure 3.
Entorhinal cortex lesion induced ultrastructural synaptic changes in DG and CA3 subfields. (A) Three-dimensional reconstructions of synapses (based on SBF-SEM) onto proximal and distal apical dendrites in the dentate gyrus (postsynaptic compartment, green; presynaptic compartment, red). (B) Analysis of both post- and presynaptic volumes from 3D reconstructions in proximal DG areas. A decrease in postsynaptic volume was detected after lesion while presynaptic volume remained stable (postsynaptic compartments: ncontrol = 170 postsynapses, n2hp ECL = 286 postsynapses, n3dp ECL = 223 postsynapses; presynaptic compartments: ncontrol = 163 presynapses, n2hp ECL = 243 presynapses, n3dp ECL = 158 presynapses from one representative tissue culture each; Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s post hoc correction). (C) Analysis of synaptic complexity, which is the number of postsynaptic sites per presynaptic bouton, at proximal synapses in DG. Notably, synaptic complexity increases following entorhinal cortex lesion. (D) Analysis of both post- and presynaptic volumes in distal DG areas. A decrease in postsynaptic and presynaptic volumes were detected (postsynaptic compartments: ncontrol = 54 postsynapses, n2hp ECL = 82 postsynapses, n3dp ECL = 48 postsynapses; presynaptic compartments: ncontrol = 49 presynapses, n2hp ECL = 74 presynapses, n3dp ECL = 38 presynapses from one representative tissue culture each; Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s post hoc correction). (E) Synaptic complexity at distal synapses in DG remained unchanged following lesion. (F) Three-dimensional reconstructions of synapses (based on SBF-SEM) onto proximal and distal apical dendrites in the CA3 region (postsynaptic compartment, green; presynaptic compartment, red). (G) Analysis of both post- and presynaptic volumes in proximal CA3 areas. An increase in presynaptic volume was detected while postsynaptic volumes remained unchanged (postsynaptic compartments: ncontrol = 208 postsynapses, n2hp ECL = 224 postsynapses, n3dp ECL = 219 postsynapses; presynaptic compartments: ncontrol = 159 presynapses, n2hp ECL = 202 presynapses, n3dp ECL = 168 presynapses from one representative tissue culture each; Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s post hoc correction). (H) Synaptic complexity at proximal synapses in CA3 remained widely unchanged following lesion. (I) Analysis of both post- and presynaptic volumes in distal CA3 areas. A decrease in postsynaptic volume was evident while presynaptic volumes remained unchanged (postsynaptic compartments: ncontrol = 99 postsynapses, n2hp ECL = 120 postsynapses, n3dp ECL = 120 postsynapses; presynaptic compartments: ncontrol = 77 presynapses, n2hp ECL = 98 presynapses, n3dp ECL = 93 presynapses from one representative tissue culture each; Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s post hoc correction). (J) Despite a trend towards reduced complexity, distal synapses in CA3 remained widely unchanged following entorhinal cortex lesion. Graphs depict box plots (box: 25–75 percentile; whiskers: 10–90 percentile; line indicates median), values outside this range were indicated by individual dots (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, ns—non-significant difference).