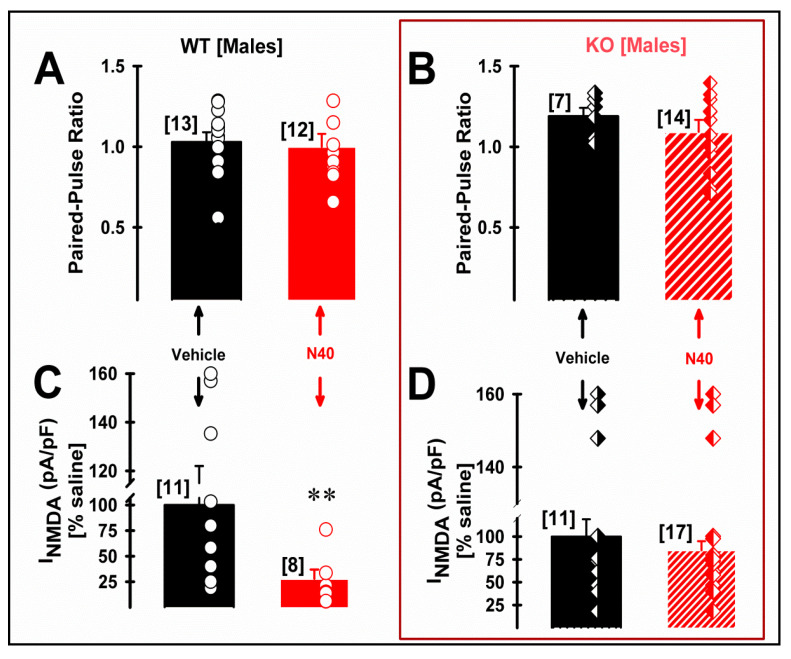
Figure 4.
Systemic noribogaine (Noribo 40; N40) treatment reduced NMDA-mediated current density in mPFC pyramidal neurons from male mice. (A,B) Graphs showing saline (black bars) and N40 (red bars) administration effect on mean EPSC paired-pulse ratio during 10 Hz stimulation (i.e., fraction of EPSC2/EPSC1 amplitudes) recorded from layer V mPFC pyramids from male WT (left plot) and 5HT2A KO (right plot) mice, respectively. Individual paired-pulse ratio values are shown for each treatment as overlying (WT), rhombi (5HT2A KO) on each bar. No significant differences were observed comparing PPR values. (C,D) Graphs showing saline (black) and N40 (red bars) administration effects on mean NMDA-mediated current density (pA/pF) values from male WT (left plot) and 5HT2A KO (right plot) mice. Individual NMDA-mediated current density values are shown for each treatment as overlying circles (WT), rhombi (5HT2A KO) on each bar. Note how N40 was able to significantly reduce the NMDA current density only in pyramidal neurons from WT male mice (see Table 1 for statistical comparisons). ** Mean INMDA current-density values were significantly smaller in KO compared to WT (post-hoc Tukey test; q = 6.2, p < 0.01). The values indicate mean ± SEM. The number of cells recorded for each group were included in brackets on top of each bar.