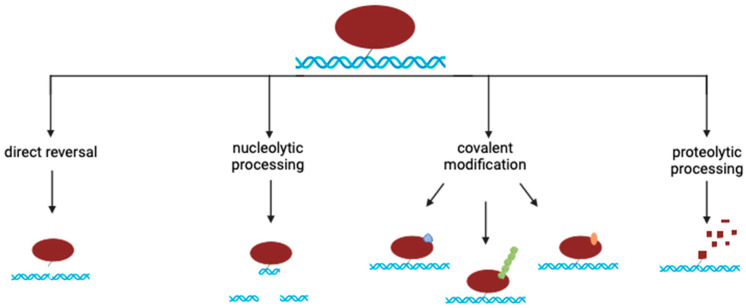
Figure 1.
Enzymatic processing of DNA–protein crosslinks. The four types of enzymatic processes that modify DPCs are depicted. Direct reversal involves the hydrolysis of the covalent bond between the DNA and the crosslinked protein (catalyzed by proteins like TDP1 and TDP2). Nucleolytic processing involves the direct incision or excision of the DNA surrounding the DNA protein crosslink (catalyzed by nucleases like Mre11 and CtIP). The covalent modification involves the covalent attachment of proteins like SUMO (blue), ubiquitin (green), or chemical groups like ADP-Ribose (orange) as monomers or polymers onto the crosslinked protein (catalyzed by proteins like Ubiquitin E3 Ligase, SUMO E3 Ligase, and PARP1). Proteolytic processing involves the proteolytic digestion of the DNA-crosslinked protein (catalyzed by the proteasome or proteases like SPRTN and ACRC).