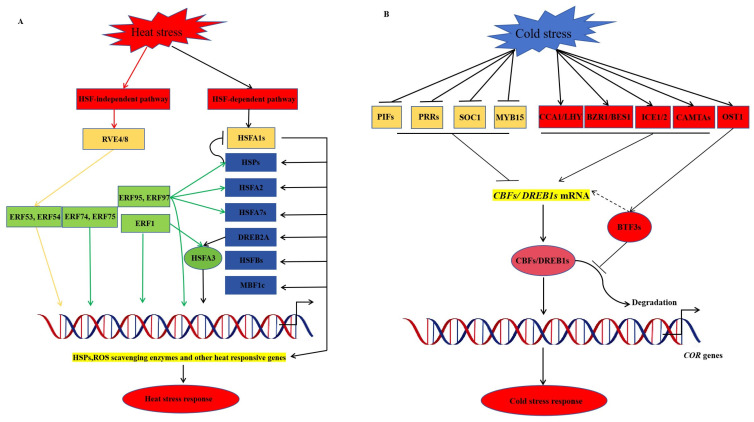
Figure 2.
AP2/ERF transcription factor-mediated temperature stress response model in plants. (A) The AP2/ERF transcription factor-mediated heat stress response model. In the HSF-independent pathway, REVEILLE4 and 8 (RVE4/8) are the major transcription factors that regulate the downstream expression of ERF53 and ERF54 and mediate plant heat tolerance. In the HSF-dependent pathway, heat stress induces the expression of HSFA1, which is a master regulator of transcriptional regulation. Under non-stress conditions, heat-shock proteins (HSPs) repress HSFA1 expression, such as HSFA2, HSFA7, DREB2A, HSFBs, and multiprotein bridging factor 1c (MBF1c), which are involved in a key transcriptional regulatory cascade. DREB2A further activates HSFA3, which activates or fine-tunes the expression of HSPs, ROS scavenger enzymes, and other HSR gene expressions. (B) The AP2/ERF transcription factor-mediated cold stress response model. Cold stress induces the expression of C repeat binding factor/dehydration response element binding protein 1s (CBF/DREB1s). CBFs/DREB1 genes are regulated by multiple transcription factors and integrate multiple signalling pathways. The light signalling components Phytochrome-interacting factors (PIF3, PIF4, and PIF7), the circadian oscillator component Pseudo response regulator (PRR9, PRR7, and PRR5), as well as other transcription factors such as Suppressor of overexpression of constans 1 (SOC1) and MYB transcription factor MYB15, negatively regulate CBFs/DREB1 gene expression. The genes CCA1, LHY, BR, BZR1/BES1, ICE1, ICE2, CAMTA, and other transcription factor inducers directly enhance the expression of CBF/DREB1 by binding to its promoter region. The protein stability of CBF/DREB1 is positively regulated by basic transcription factor 3 (BTF3) phosphorylated by Open stomata 1 (OST1). AP2/ERF transcription factor ERF regulates CBF/DREB1 expression by binding directly and indirectly to the CBF/DREB1 promoter. ERF also directly regulates the expression of other COR genes by binding to their promoters. Arrow ends indicate the activation effect; bar ends indicate the repression effect.