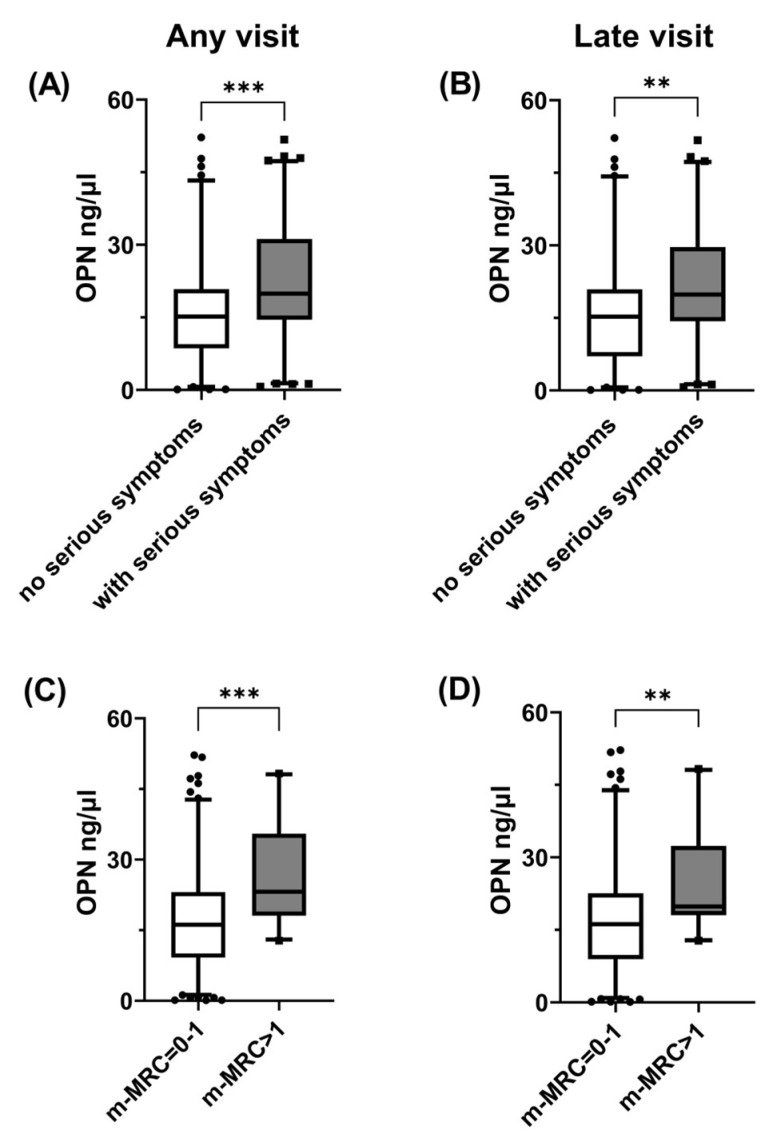
Figure 2.
Increased plasma OPN levels were associated with severe post-acute COVID-19 sequelae.OPN levels from 181 plasma samples obtained during follow-up visits from 122 previously hospitalized COVID-19 patients were compared in the absence and presence of a serious symptom combination (defined as at least one of the following: dyspnea, fatigue and muscular weakness) at any visit, n = 89 vs. n = 92 (A), or at visits occurred 90 days or more (late visits) post-symptom onset, n = 80 vs. n = 74 (B); dyspnea where m-MRC > 1 at any visit, n = 146 vs. n = 29 (C); and dyspnea where m-MRC > 1 at late visits, n = 126 vs. n = 23 (D). Data are presented as 5–95 whisker plots with median, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. OPN: osteopontin, m-MRC: modified Medical Research Council dyspnea scale.