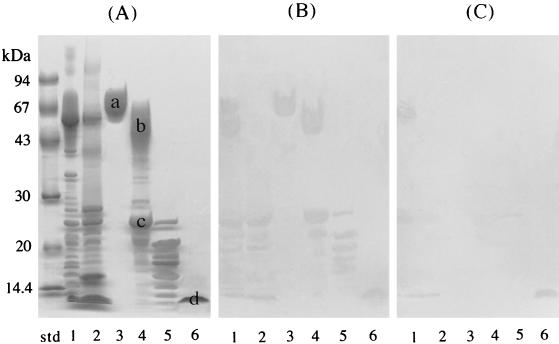
FIG. 5.
Inhibitory effect of PRP-C on the binding of fimbriae to salivary components. Since the peptide PRP-C (PQGPPPQGGRPQGPPQGQSPQ) was found to be significantly inhibitory for the fimbria-PRG interactions, the overlay assays as shown in Fig. 1 were performed with the addition of PRP-C. (A) SDS-PAGE profiles of salivary components which bound to fimbriae. (B) The overlay assay performed as shown in Fig. 1 without the addition of PRP-C. The replica membrane was incubated with 5 ml of fimbriae (41 μg/ml, 1 nmol/ml of KCl buffer). (C) The overlay assay performed with the simultaneous additions of PRP-C (100 nmol/ml) and fimbriae (1 nmol/ml) in 5 ml of KCl buffer. Lanes: std, molecular mass standard; 1, parotid saliva; 2, submandibular and sublingual saliva; 3, H-PRG; 4, L-PRG–PRP1 fraction; 5, small-molecular-size components that bind to fimbriae; 6, statherin.