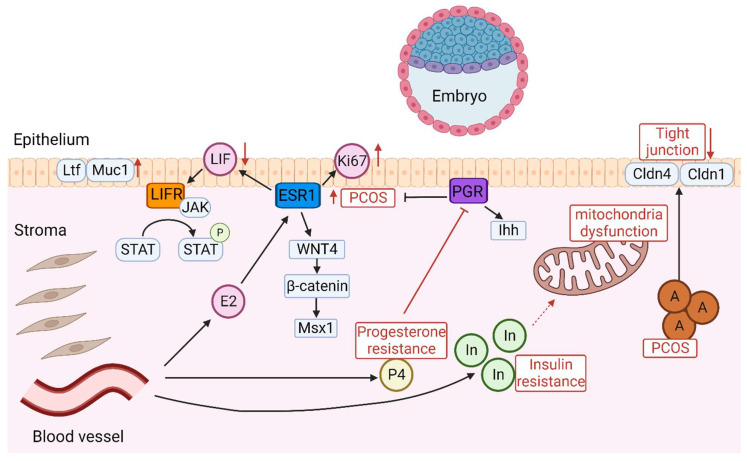
Figure 1.
Diagram of the intricate signaling pathways involved in embryo implantation. In PCOS, abnormal expression of ESR1 increases Ki-67 expression in the endometrial epithelium and stroma, leading to decreased endometrial receptivity. LIF triggers the activation of JAK which in turn activates signal transducer and activator of STAT3 through phosphorylation. The role of the LIF-STAT3 pathway is characterized by inactivation in PCOS, which leads to the production of Ltf and Muc1, suggesting that the endometrium is in a non-receptive state. The dysregulation of the Wnt/β-catenin/Msx1 pathway impairs endometrial receptivity in PCOS and Msx1 is increased. Insulin resistance contributes to progesterone resistance and exacerbates issues with endometrial functionality. The abnormal expression of Ihh signaling in PCOS is depicted as a key factor affecting endometrial receptivity. Elevated androgen levels impact the integrity of tight junctions in the endometrial epithelium by decreasing Cldn4 and Cldn1. Insulin resistance impairs endometrial receptivity in PCOS, leading to mitochondrial dysfunction. A: Androgen; P4: Progesterone; E2: Estrogen; In: Insulin; P: phosphorylation.