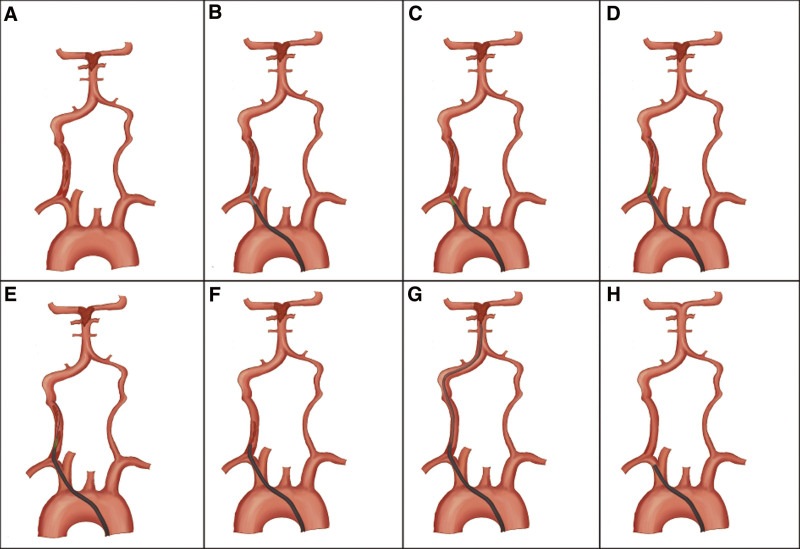
Figure 1.
(Schematic diagram.). (A) Acute occlusion of the origin of the right vertebral artery, secondary thrombus occlusion of the basilar artery. (B, C) The guidewire was passed through the vertebral artery occlusion and the Neuron MAX 088 inner dilator was exchanged to the proximal vertebral artery occlusion. (D, E) The Neuron MAX 088 inner dilator passed along a guidewire through occluded vertebral arteries, and the Neuron MAX 088 guiding catheter was subsequently advanced over the inner dilator, through the occluded segment. (F, G, H) Firstly, negative pressure suction was performed on the Neuron MAX 088 guiding catheter, followed by a suction catheter up to the basilar artery occlusion to extract the thrombus. After the vertebral artery recanalization, the residual stenosis of the occluded segment was observed to determine whether to undergo stenting.