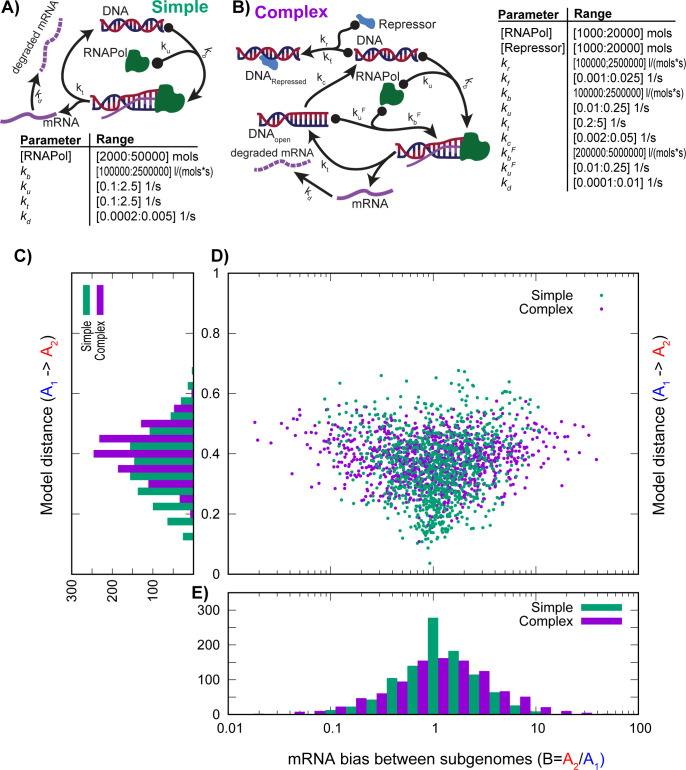
Fig 3. Exploring the state space of expression models for allopolyploids.
In A&B, we propose two meta-models of gene expression, a simple one (A) involving only the polymerase binding a target gene (similar to Fig 1A but without DNA breathing), and a more complex one that follows Fig 2 with slightly different parameter values (Methods). In each case, we generate two random models A1 and A2 by selecting uniform random values for the model parameters across the ranges listed (Methods). After computing the steady state mRNA concentration for A1, we use an approximate gradient method to bring A2 to equal steady state mRNA concentration with A1 (Methods). The resulting parameter values are normalized and the Euclidian distance between A1 and A2 is computed (Methods). We then construct an allopolyploid hybrid of A1 and A2 and compute resulting mRNA bias B C. Distribution of model-pair distances for 1000 simulations of the simple and complex models from A&B. On x is the distance between the model pairs (y-axis in D), on y are the frequencies of those distances. D. One thousand random pairs of genome models were created from each meta-model and their hybrids simulated. The plot shows the relationship between the distance between the model pairs (y-axis) and expression bias B (x-axis: note the log scale). E. Histograms of B, plotted on a log-scale (c.f., C).