Figure 6. Image processing influences quantification of arterial FDG uptake.
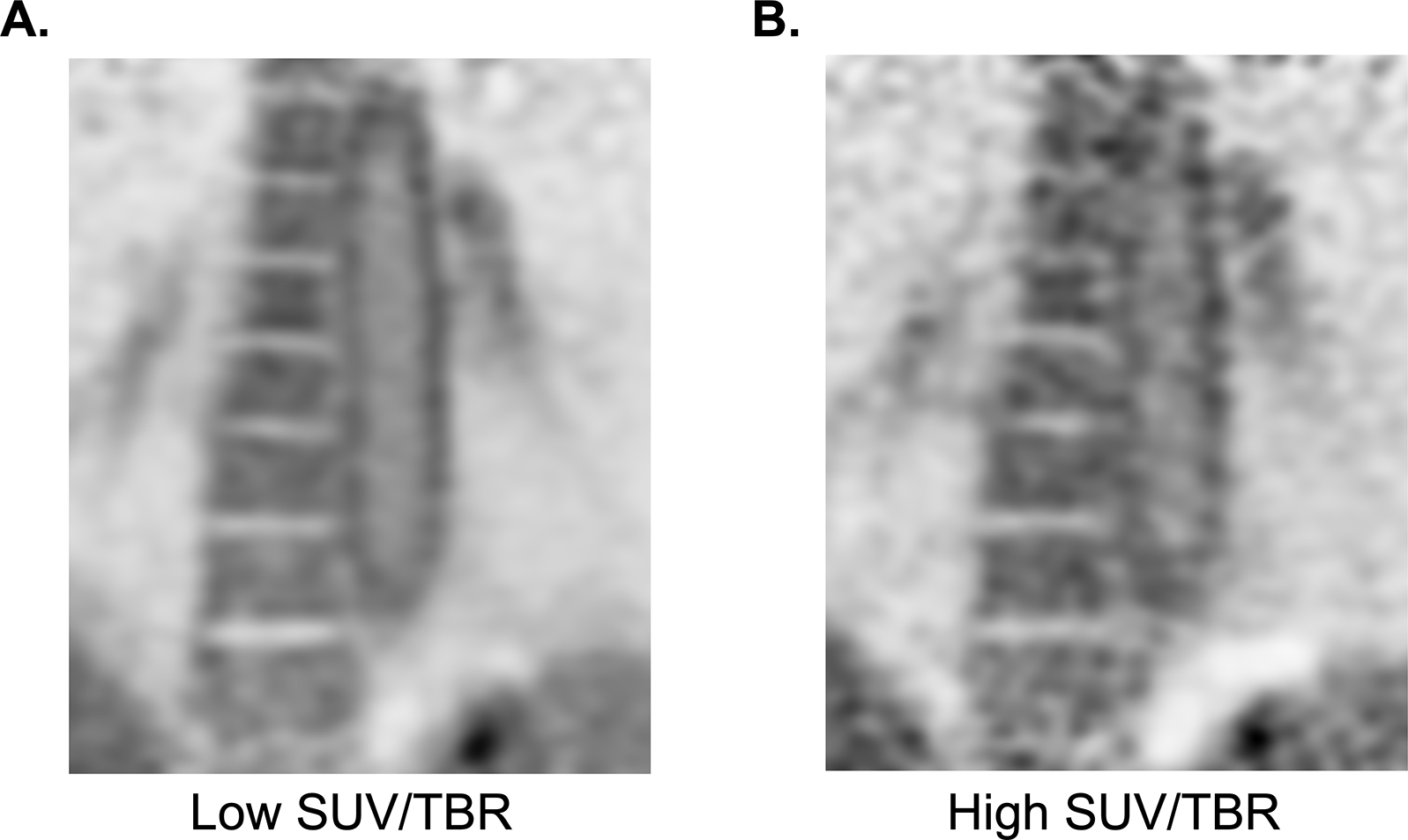
Two coronal reconstructions of the same raw FDG PET data of the descending thoracic aorta. Left frame (A) showing reconstruction of the full time of an extended data acquisition (~20 minutes) compared to the right frame (B) showing the typical acquisition in clinical PET, of no more than 5 minutes per image frame. The typical acquisition results in higher maximum SUV and TBR of structures due to image noise alone because it is sampling the highest point in high statistical noise. This patient does not have a history of LVV, and the activity in the aorta is likely due only to physiologic smooth muscle cell activity. Differentiation with pathologic uptake in this case is due the pan-arterial uptake that scales with relative size of the arteries throughout the patient’s body.
