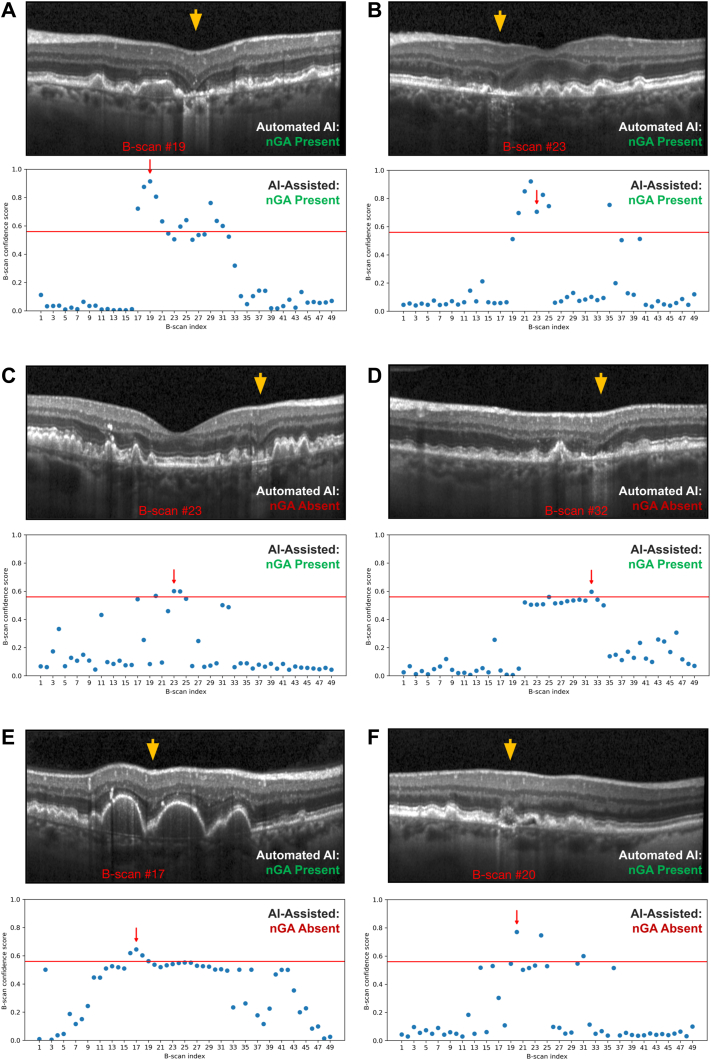
Figure 7.
Examples of cases in this study, with a selected OCT B-scan shown on the top of each case (with region of interest indicated by the orange arrow), and a plot of the confidence scores of having nascent geographic atrophy (nGA) at each of the 49 B-scans from the OCT volume scan shown on the bottom (with the selected B-scan shown on the top indicated by the red arrow, and the threshold for identifying B-scans requiring manual review that resulted in a 0.98 specificity shown as the horizontal red line). The first 2 cases (A and B) represent cases where the fully automated artificial intelligence (AI) model considered the volume scan to have nGA, and where the AI-assisted approach also identified nGA as being present. The next 2 cases (C and D) show examples where the fully automated AI model did not consider nGA as being present, but the manual review of selected B-scans with the AI-assisted approach led to the correct detection of nGA. The 2 final cases (E and F) represent cases deemed to have nGA by the fully automated AI model, that were correctly identified as not having nGA following manual review of the selected B-scans with the AI-assisted approach. The orange arrows indicate the region of interest in (A and B), they are nGA lesions located by manual review and also highlighted by AI (Gradient-weighted Class Activation Mapping, see Fig 4); in (C and D), they are nGA lesions located by manual review only. In (E and F), they are suspicious nGA lesions suggested by AI, but rejected by human review.