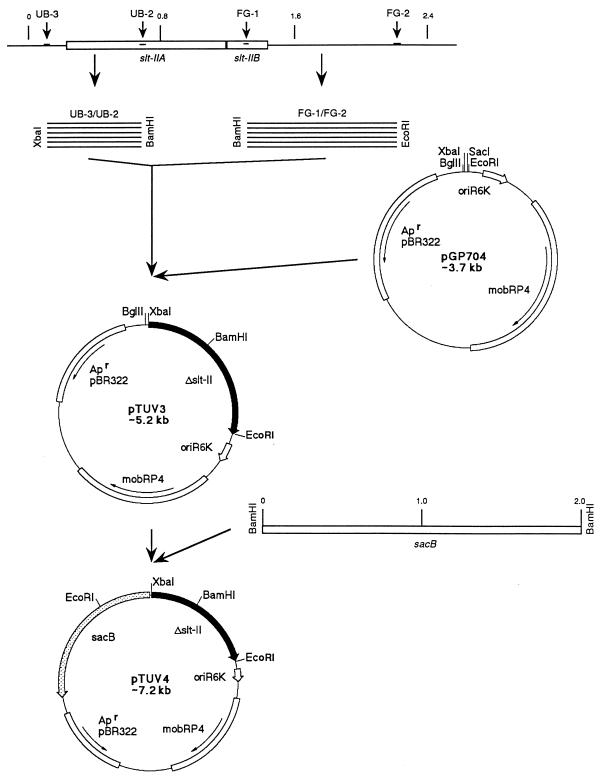
FIG. 1.
Construction of pTUV4. PCR fragments generated from E. coli 86-24 by utilizing the primer pairs UB-3–UB-2 (610 bp) and FG-1–FG-2 (870 bp) were eluted from agarose gels and digested with XbaI and BamHI or BamHI and EcoRI, respectively. Cloning of these fragments into pGP704, digested with XbaI and EcoRI, created a mutagenized slt-ii gene copy, harboring a 589-bp internal deletion. The resulting plasmid was named pTUV3. Introduction of the sacB selection system into BglII-digested pTUV3 yielded pTUV4. Δslt-ii, deletion mutation of the slt-ii gene; oriR6K, origin of replication from plasmid R6K; mobRP4, oriT from plasmid RP4 (allows mobilization of pTUV4 using the RP4 broad-host-range mobilization system); Apr, gene encoding ampicillin resistance from plasmid pBR322; sacB, gene from B. subtilis encoding the enzyme levansucrase (positive selection system).