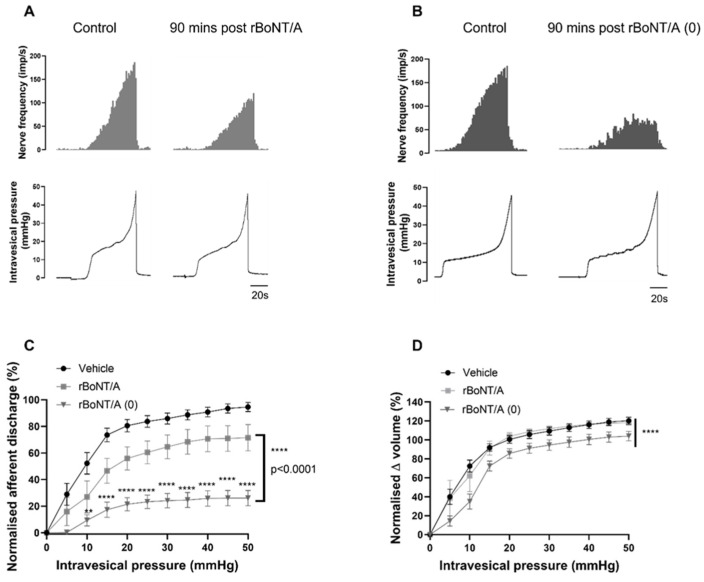
Figure 5.
The effects of recombinant active rBoNT/A and inactive rBoNT/A (0) on distension-induced afferent signalling. (A) A representative trace showing the response of afferent nerves to distension prior to (control) and 90 min after rBoNT/A treatment. (B) A representative trace showing the response of afferent nerves to distension prior to (control) and 90 min after rBoNT/A (0) treatment. (C) Distension-induced afferent responses were significantly reduced by rBoNT/A (**** p < 0.0001; n = 6; two-way ANOVA) and rBoNT/A (0) (**** p < 0.0001; n = 8; two-way ANOVA) compared to vehicle-treated preparations (n = 13). The distension-induced firing in preparations treated with rBoNT/A (0) was significantly lower than in those treated with rBoNT/A (**** p < 0.0001) (** p < 0.01). (D) The pressure–volume relationship of rBoNT/A-treated preparations was not different to that of vehicle-treated preparations (p = 0.8765; n = 6; two-way ANOVA), while rBoNT/A (0) significantly reduced the pressure–volume relationship (**** p < 0.0001; n = 8; two-way ANOVA).