Figure 9.
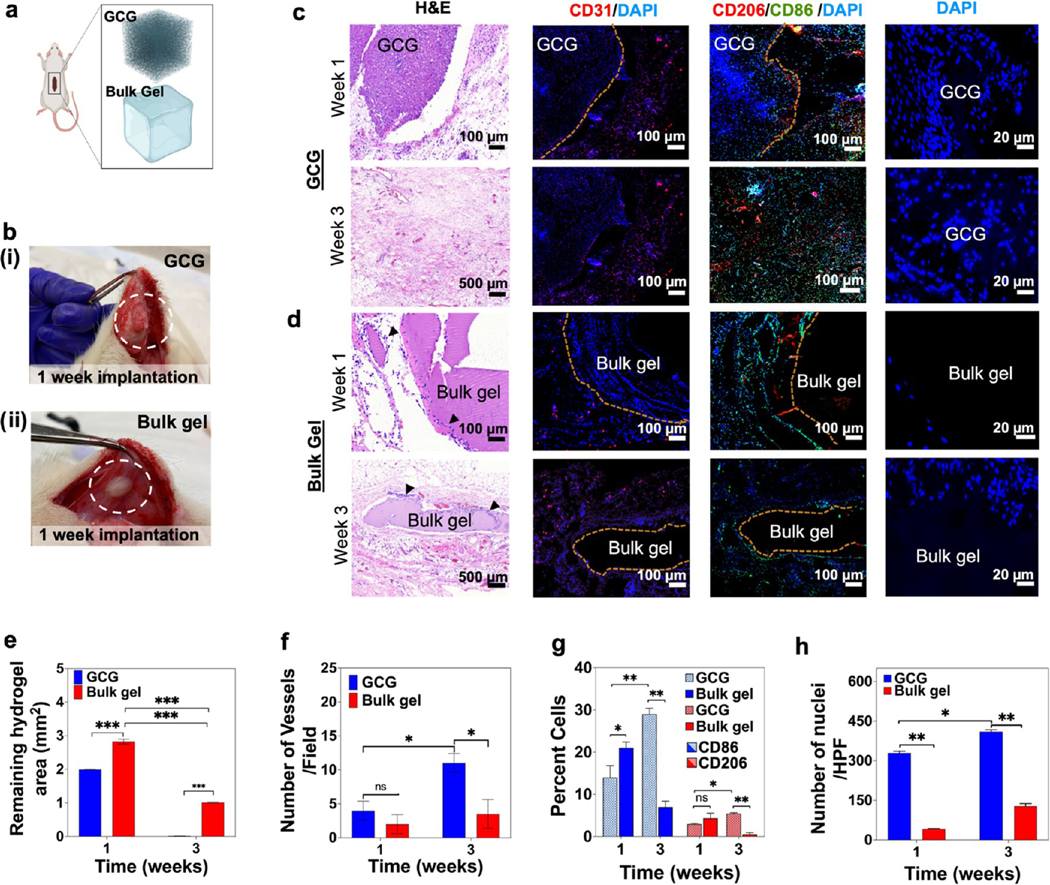
Biological characterization of a bioprinted GCG in vivo. (a) Schematics for the subcutaneous implantation of both the hydrogels. (b) GCG hydrogel (i), and bulk GelMA hydrogel (ii) explants 1 week post implantation. (c) GCG and (d) bulk GelMA hydrogel explants at 1 and 3 weeks were analyzed for cell invasion and degradation behavior (H&E), neovascularization (CD31), and macrophage induction (CD206 and CD86) along with DAPI staining. Black arrow heads in panel d (H&E) indicate host cells around the bulk GelMA hydrogel. (e–h) Semiquantification data for (e) degradation of the GCG and bulk hydrogels, (f) number of vessels, (g) percent of CD206- and CD86-stained macrophages, and (h) number of nuclei for host cell infiltration within the GCG and bulk hydrogels. (n = 3; ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05.)
