Fig 6.
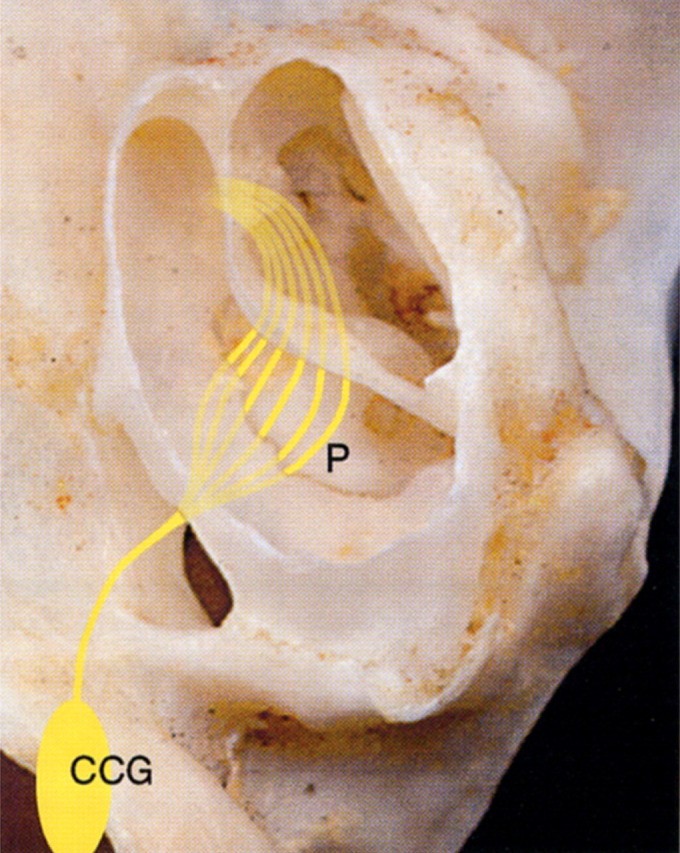
View of the ventral surface of the left petrous portion of the temporal bone with the left tympanic bulla and bony septum partially removed. The course of the sympathetic nerves that negotiate the middle ear of the cat on their course from the cranial cervical ganglion (CCG) to the eye are represented diagrammatically. The lighter colored lines represent nerve fibres that pass under the endotympanic plate, and are, thus, protected from surgical trauma. The darker yellow lines represent the fibres of the tympanic plexus that extend rostrally across the promontory (P), where they are highly vulnerable to surgical trauma. Interruption of the sympathetic nerve fibres at this location will result in Horner's syndrome. [Adapted with permission from Barlow & Root (1949) Journal of Comparative Neurology 91, 195–207.]
