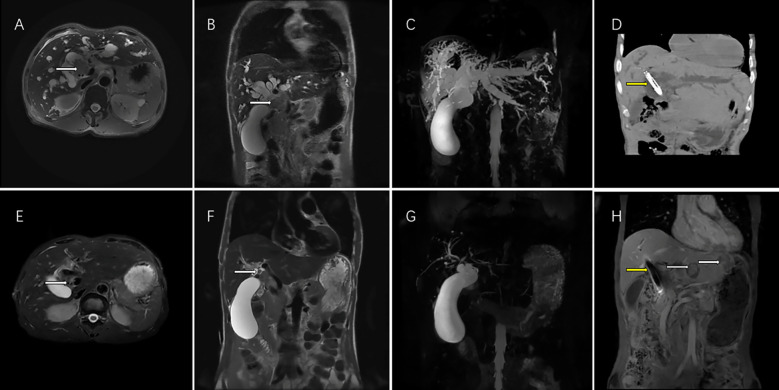
Figure 3.
This magnetic resonance (MR) images showed the imaging feature of 62-year-old men with perihilar cholangiocarcinoma accompanied by malignant obstructive jaundice. T2 weighted cross sectional imaging (A) and T2 weighted coronal imaging (B) showed the bile duct tumor of the hilar region (white arrow) with bile duct dilatation before interventional treatment plus lenvatinib with PD-1inbhibitor therapy; Magnetic resonance cholangial pancreatography (MRCP) showed thick intrahepatic dilated bile ducts and a large gallbladder (C); Computed tomography showed biliary stenting with iodine-125 seed strand (yellow arrow) were in good position 1 month after the operation (D). T2 weighted cross sectional imaging (E), T2 weighted coronal imaging (F) showed that the bile duct tumor volumes of the hilar region shrank (white arrow), the bile duct returned to normal size and achieved PR according to the mRECIST criteria after 5 courses of interventional treatment plus lenvatinib plus PD-1inbhibitor therapy. MRCP showed the normalization of the intrahepatic bile ducts after treatment (G). Although hepatic portal tumor was well controlled (yellow arrow), two new intrahepatic metastatic lesions appeared (yellow arrow) in the left liver 12 months after interventional treatment plus lenvatinib with PD-1inhibitor therapy and achieved PD according to the mRECIST criteria (H). PR, partial response; mRECIST, the Modified Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors. PD, progression disease; mRECIST, the Modified Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors; PD-1, programmed death-1.