Fig. 1.
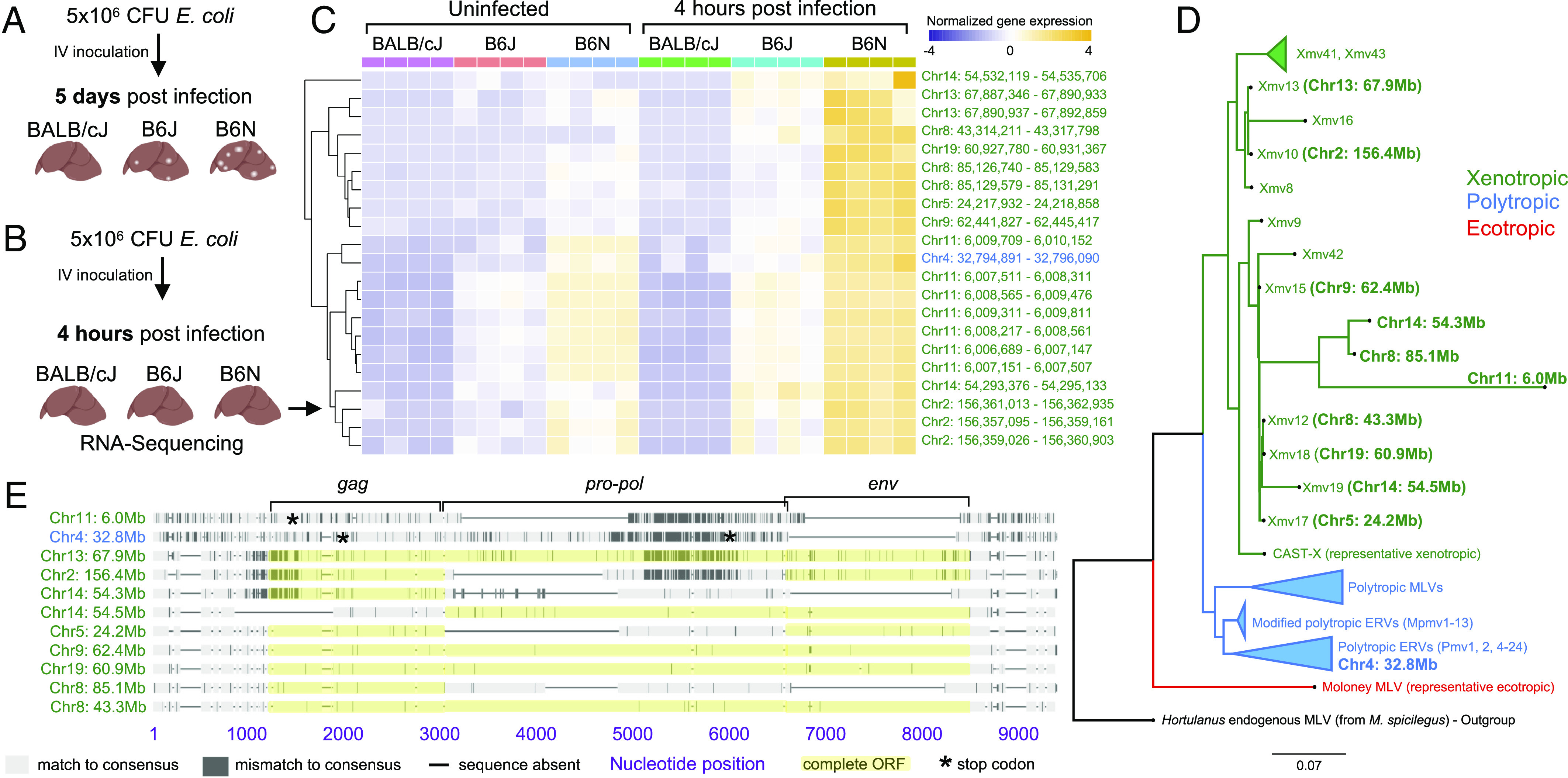
ERV expression correlates with abscess susceptibility. (A) Schematic of variation in abscess susceptibility in BALB/cJ, B6J, and B6N female mice. (B) Schematic of RNA-Sequencing experiment. (C) Z-score normalized expression of transcripts that are induced by infection in B6N mice and whose expression correlates with abscess susceptibility. The complete dataset, including non-ERV genes, is in Datasets S1 and S2. Coordinates are from GRCm38. (D) Maximum likelihood tree of abscess-associated and representative ERV loci in B6J. Loci identified in this study are in bold and those identical to previously known loci are in parentheses [e.g., Xmv13 (Chr13: 67.9 Mb)]. Four loci lack env and do not match previously known ERVs (3). For clarity, one xenotropic and several polytropic MLVs are represented as single, collapsed branches (triangles). (E) Sequence alignment of the 11 abscess-associated MLV loci compared to their consensus.
