Fig. 1.
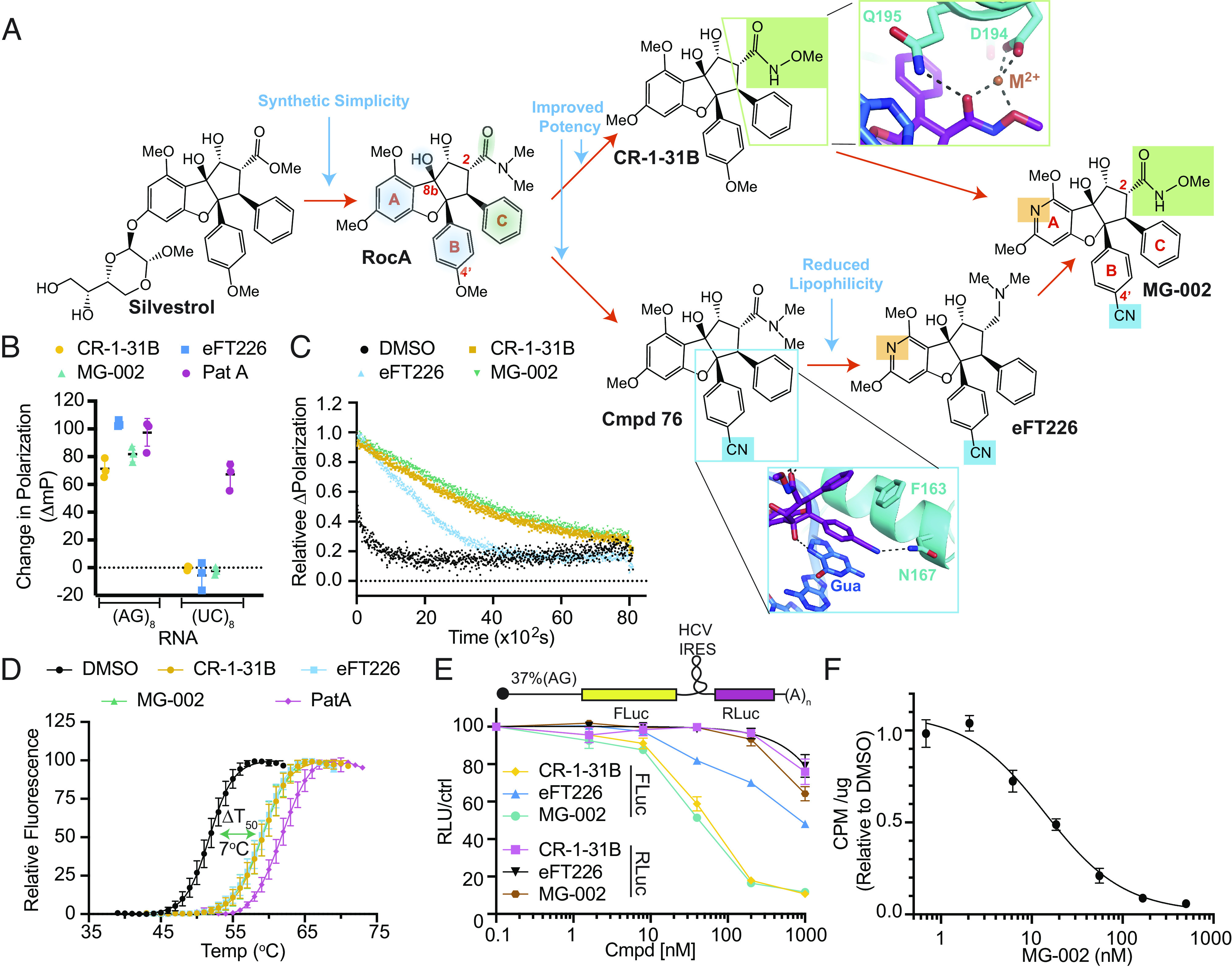
Design of an eIF4A inhibitor (MG-002) that potently inhibits cap-dependent mRNA translation. (A) Schematic outlining the rationale behind MG-002 development. RNA- (blue shading) and eIF4A1 (green shading)-interacting regions are highlighted on the RocA structure. Insets show close in views of a model of the MG-002 hydroxymate and nitrile groups, based on the RocA-bound crystal structure of eIF4A1 (26). (B) Assessing compound-induced clamping of eIF4A1 to FAM-labeled RNA of the indicated nucleotide composition by fluorescence polarization assay. The ΔmP (change in polarization) obtained with eIF4A1•AMPPNP •poly (NN)8 RNA was measured for the indicated compounds at 10 µM. The ΔmP obtained relative to dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) is shown (n = 3 ±SD). (C) Relative dissociation of pre-formed eIF4A1•ATP•Cmpd•FAM-poly (AG)8 complexes measured as a function of time in the presence of 1,000-fold molar excess poly (AG)8 RNA. DMSO, t1/2 ~4.1 ± 1 min; CR-1-31B (10 µM), t1/2 ~59 ± 6.5 min; MG-002 (10 µM), t1/2 ~68 ± 2.8 min; eFT226 (10 µM), t1/2 ~ 27 ± 5.8 min. Error values were calculated from the 95% CI. (D) Differential scanning fluorimetry analysis of eIF4A1 (8 µM) in the presence of the indicated compounds (15 µM), 15 µM poly (AG)8, and 1 mM AMPPNP. The transition midpoint temperature shifts (ΔT50) are: CR-1-31B, 7.3 °C; eFT226, 7 °C; MG-002, 7.2 °C; PatA, 10 °C (n = 3 ±SD). (E) Inhibition of cap-dependent (FLuc) and independent (RLuc) translation was measured in response to the indicated compounds in Krebs-2 translation extracts programmed with the noted bicistronic mRNA. IC50s toward inhibition of FLuc synthesis from (CAG)-FF/HCV-IRES/Ren mRNA were: CR-1-31B, 54 ± 4 nM; eFT226, 813 ± 91 nM; MG-002, 43 ± 4 nM (n = 2 ±SD). (F) eHap1 cells were incubated in the presence of the indicated concentrations of compound for 1 h. During the last 15 min of incubation, 35S-Met was added followed by TCA precipitation and quantitation of 35S-Met incorporation into protein (n = 3 ±SD).
