Fig. 7.
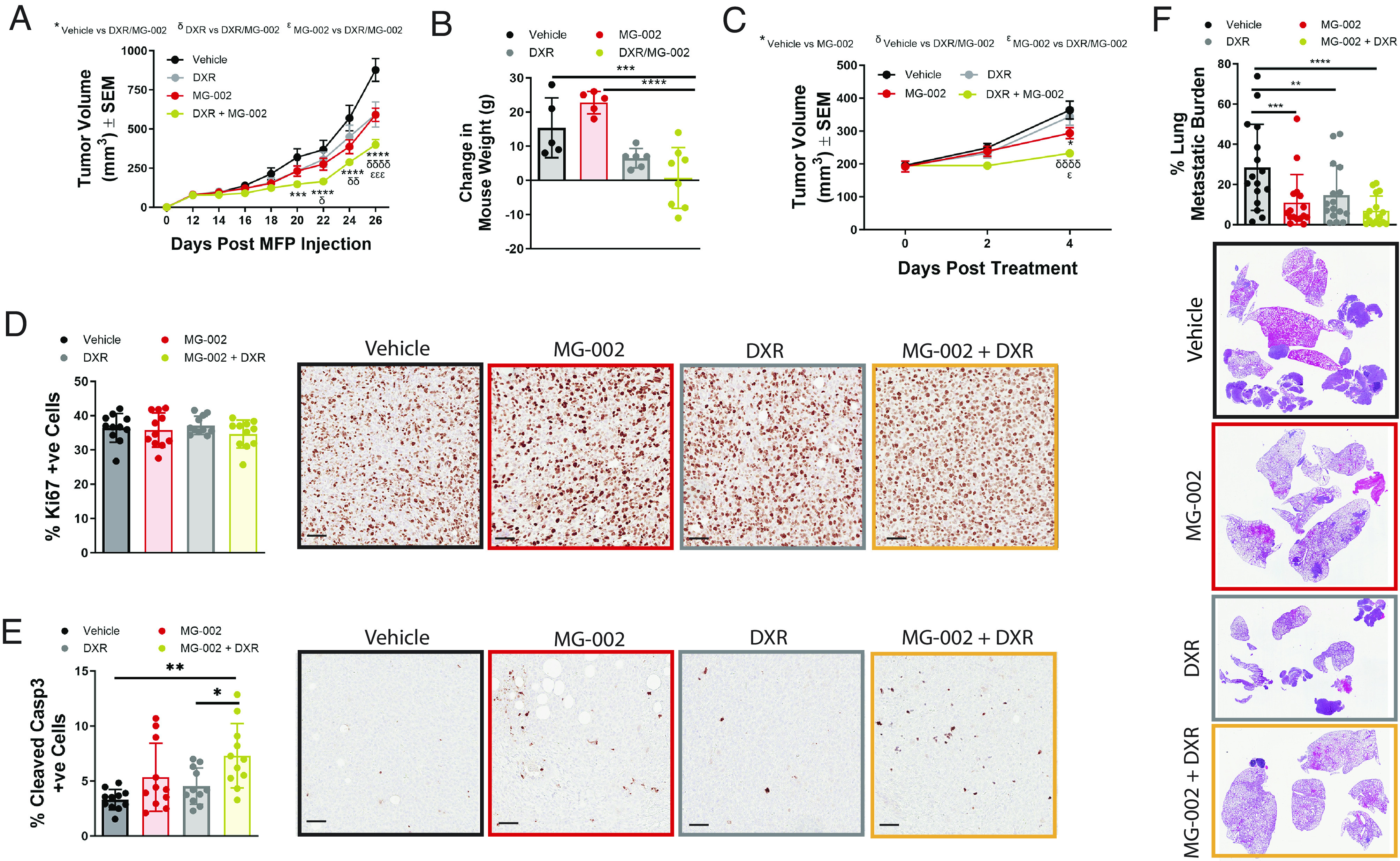
MG-002/DXR combination therapy reduces the growth of established primary TNBC breast tumors and lung metastases. (A) 4T1-526 mammary tumors were allowed to develop in the mammary fat pads of Balb/c mice and when tumors reached ~100 mm3, animals were randomized into four groups: 1) 0.5 mg/kg MG-002 PO; 2) 2.5 mg/kg DXR IP; 3) MG-002/DXR combination treatment using the same concentrations; and 4) vehicle control. Animals were treated every 3 d until the experimental endpoint (n = 10 to 14 tumors/group). The data are shown as average tumor volume ± SEM. (B) At the experimental endpoint, each animal in panel A was measured for the average change in weight from the beginning to the end of the study. (C) Tumors were treated as described in panel A, but mice were sacrificed 4 d after the start of drug treatment. (D and E) Tumors from the mice harvested in panel C were analyzed by immunohistochemistry using (D) Ki67 or (E) cleaved caspase-3 specific antibodies (n = 11 tumors per group). (F) Mice with established metastases (as outlined in Fig. 6C) were randomized into four groups and treated as outlined in panel A. The metastatic area in the lungs was quantified from H&E-stained sections (n = 16 mice/group), and the average metastatic burden is presented ±SD. Statistical analysis was performed with a two-way ANOVA (Tukey’s multiple comparisons test).
