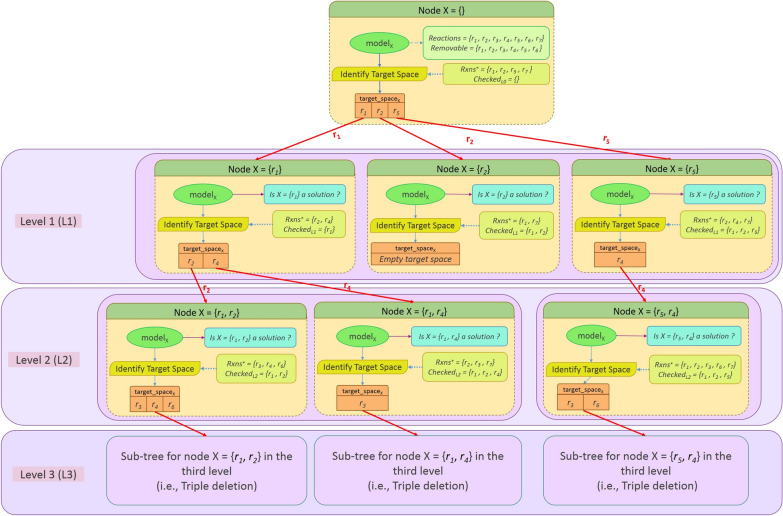
Fig. 1.
The traversal tree: All possible solutions are identified through a depth-first traversal of the tree. First, the identifyTargetSpace function is applied in the root node to the reduced wild-type network to determine the target space. Each reaction in this set is individually selected and removed from the network in Level 1. For each deleted reaction (or equally node) in Level 1, the identifyTargetSpace function is recalled to obtain the target space for the next level. For simplicity, we show only two levels of the traversal of the tree, which is enough to identify all single and double deletions