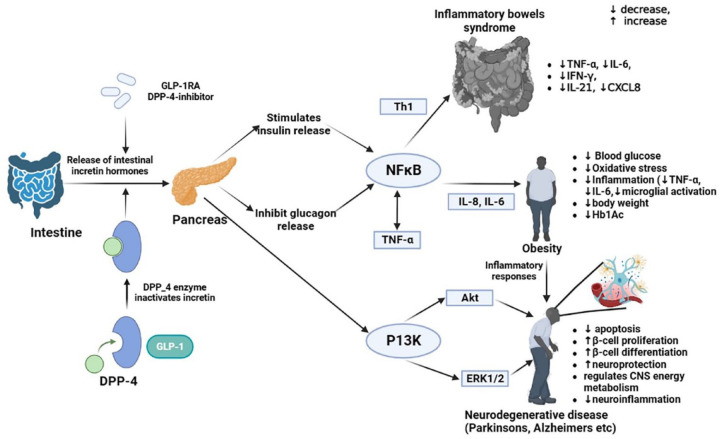
Figure 1.
A schematic representation of the mechanism of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists (GLP-1RA) inducing anti-inflammatory response while treating obesity, neurodegenerative disorders, and IBD. The role of GLP-1RA in obesity, neurodegenerative and IBD disorders is accomplished by NFκB and PI3K-Akt pathways, leading to the anti-inflammatory effect, by downregulation the pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines like IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α, IL-21, and IFNγ. As a result of these pathways, various tissues are more anti-oxidative, which reduces obesity, neurodegenerative, and IBD complications. In neurodegenerative conditions, β-cells undergo differentiation which enhances their neuroprotective capabilities and lessens the extent of neuroinflammation.
Akt, activating receptor tyrosine kinase; CXCL8, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 8; DPP-4, dipeptidyl peptidase-4; ERK1/2, extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases 1 and 2; GLP-1, Glucagon-like peptide-1; GLP-1RA, Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists; IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; IFN-γ, Interferon-γ; IL-8, interleukin-8; IL-6, interleukin-6; IL-21, interleukin-21; NFκB, Nuclear Factor-kappa B; PI3k, phosphoinositide-3-3kinase-protein kinase; Th1, T-helper-1; TNF-α, Tumor necrosis factor- α.