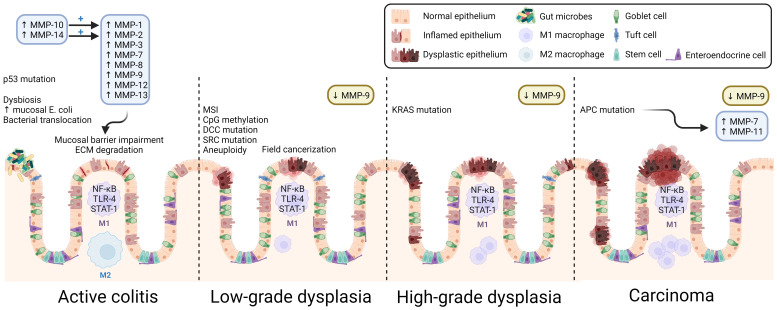
Figure 3.
Overview of CAC pathogenesis. Many MMPs are over-expressed, and their activity upregulated in active colitis. MMP-induced mucosal damage, inflammatory dysbiosis, early p53 mutation, and other results of DNA damage promote dysplastic changes. Because the inflammatory insult is widespread, CAC exhibits field cancerization, and multiple malignant foci form in the affected tissue. As dysplasia progresses, the population of colonic macrophages shifts toward the pro-inflammatory M1 macrophage subtype. Despite its membrane-degrading effects in colitis, MMP-9 is consistently found to be downregulated in CAC and acts as a tumor suppressor. ECM, extracellular matrix; MSI, microsatellite instability. Created with BioRender.com.