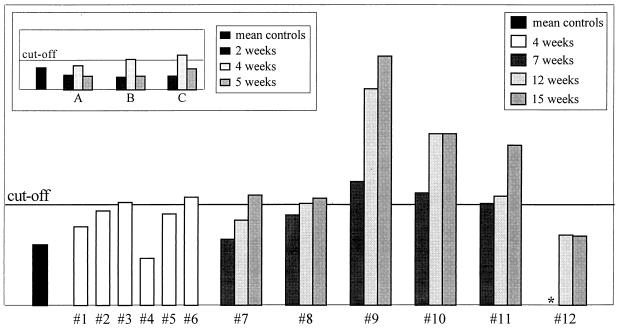
FIG. 1.
H. pylori serology. OD readings are plotted versus individual guinea pig serum samples analyzed in duplicate. The cutoff line is the mean plus 3 SD of the OD readings of sham-dosed control guinea pigs at 4, 7, 12, and 15 weeks postdosing. One-third of the infected guinea pigs were seropositive at 4 weeks postinfection. OD readings for each of the six 15-week infected guinea pigs at 7, 12, and 15 weeks postinfection are plotted. One animal remained seronegative for the 15-week duration of the study. (Inset) To determine whether seropositivity correlated with active infection or merely with exposure to H. pylori antigen, three adult female guinea pigs (A, B, and C) were dosed with killed H. pylori antigen, following the same dosing schedule and receiving the same quantity of antigen as the experimentally infected group. The cutoff line is the mean plus 3 SD of the OD readings from these guinea pigs prior to dosing. Two of the three guinea pigs were borderline seropositive at 4 weeks but seronegative at 5 weeks postexposure (a decreasing titer), in contrast to the H. pylori-infected guinea pigs, who had rising titers for the duration of their infection. ∗, sample unavailable.