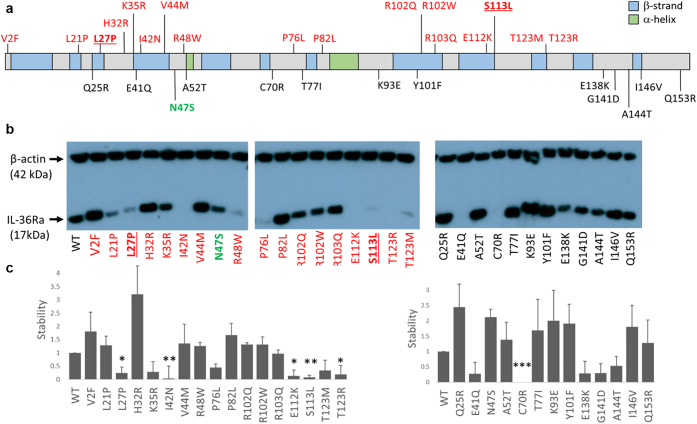
Figure 1.
Effects of IL36RN sequence variants on protein stability. (a) Schematic showing the position of the examined variants. Changes observed in affected individuals are highlighted in red, with the recurrent p.Pro27Leu and p.Ser113Leu mutations in underlined font. The common p.Asn47Ser variant is shown in green, whereas rare population variants from the gnomAD database are in black. (b) Representative western blots showing the accumulation of wild-type (WT) and mutant IL-36Ra, after the transfection of the relevant cDNA constructs into HeLa cells. (c) Densitometry results for patient (left) and population (right) variants. Stability was calculated as the IL-36Ra/β-actin ratio normalised to wild-type values. Results are presented as means ± SD for 3 independent transfections. ∗P<0.05; ∗∗P<0.01; ∗∗∗P<0.001.