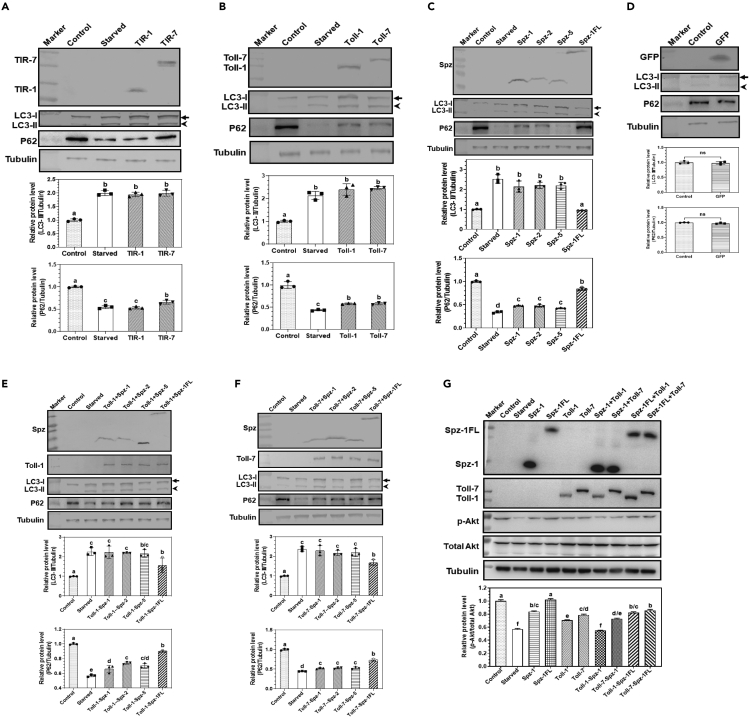
Figure 1.
Overexpression of Toll, Spz, and Toll-Spz complex in S2 cells induces autophagy
(A‒F) Detection of LC3-I, LC3-PE (LC3-II), and P62 proteins in S2 cells overexpressing Toll, Spz, and Toll-Spz complex by immunoblotting. S2 cells stably expressing RFP-GFP-LC3 were cultured in complete medium without treatment (control), or cultured in PBS instead of complete medium for 6 h (starved), or transfected with pMT-TIR-1-V5, pMT-TIR-7-V5 (A), pMT-Toll-1-V5, pMT-Toll-7-V5 (B), pMT-Spz-1-Flag, pMT-Spz-2-Flag, pMT-Spz-5-Flag, pMT-Spz-1FL-Flag (C), or pMT-GFP-V5 (D), or co-transfected with pMT-Toll-1-V5 or pMT-Toll-7-V5 with pMT-Spz-1-Flag, pMT-Spz-2-Flag, pMT-Spz-5-Flag, or pMT-Spz-1FL-Flag (E and F), then recombinant proteins were detected by mouse anti-V5 and mouse anti-Flag monoclonal antibodies, respectively. In these S2 cells, P62 protein was detected by anti-Ref(2)P antibody, LC3-I and LC3-II were detected by rabbit anti-LC3 polyclonal antibody, while tubulin was detected by mouse anti-tubulin monoclonal antibody.
(G) Detection of Akt protein in S2 cells overexpressing Toll-Spz complex by immunoblotting. S2 cells stably expressing RFP-GFP-LC3 were treated as described above, total Akt (t-Akt) and phosphorylated Akt (p-Akt) in cells were detected by rabbit anti-Akt and rabbit anti-phosphor-Akt (p-Akt) polyclonal antibodies, respectively. Protein bands from at least 3 membranes were scanned for each protein using ImageJ. Data were represented as means ± SEM. Significant difference was determined by one way ANOVA followed by a Tukey’s multiple comparison tests using GraphPad Prism, with different letters indicating significant difference (p < 0.05) and identical letters for non-significant (p > 0.05). Significant difference was also determined by the student’s t test, ns for non-significant.