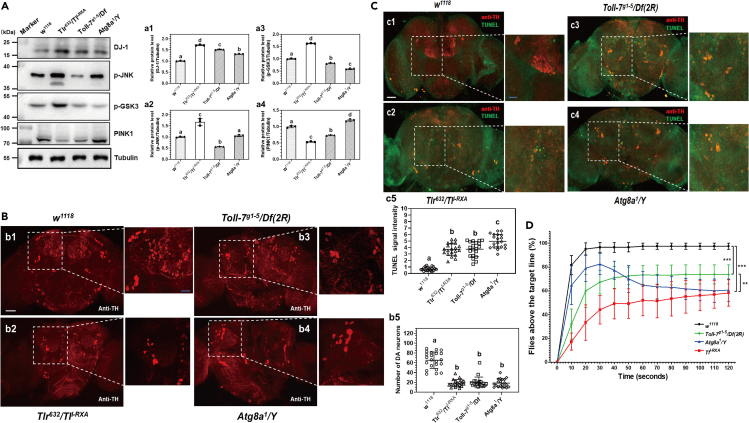
Figure 7.
Toll-1 and Toll-7 regulate DA neuron survival in Drosophila brain and control fly climbing ability
(A) Detection of DJ-1, JNK, GSK3, and PINK1 proteins in Drosophila adult brain by immunoblotting. DJ-1, phosphorylated JNK (p-JNK), phosphorylated GSK3 (p-GSK3), and PINK1 proteins in the brains of the control flies (w1118), Toll-1 (TlI−RXA/Tlr632), Toll-7 (Toll-7g1-5/Df(2R)), and Atg8a1/Y mutant flies were detected by immunoblotting, tubulin was detected as a loading control.
(B and C) Detection of DA neurons and apoptosis in Drosophila adult brain. Brains from different fly lines were dissected, DA neurons in the brain were labeled with anti-TH antibody. Brains from these flies were also stained with TUNEL and anti-TH antibody (C). DA neurons number was counted (B, b5) and TUNEL fluorescence intensity was quantified (C, c5) from at least 20 brains for each fly line by ImageJ. Scale bar: 50 μm in a1 to a4, 20 μm in the amplified sections.
(D) Locomotor ability of Drosophila adult flies. The w1118 flies, Toll-1, Toll-7, and Atg8a1/Y mutant flies were used for climbing assays to determine fly locomotor ability. The percentage of flies passing the threshold line is represented every 10 s over the duration of the assay. For each genotype, 10 biological replicates, each with 20 flies (a total of 200 flies), were used for the assays. Data were represented as means ± SEM. Significant difference was determined by one way ANOVA (a1–a4, b5, c5) (see Figure 1 legend) and by the Student’s t test (D, indicated by ∗ p < 0.05, ∗∗ p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗ p < 0.001).