FIG. 2.
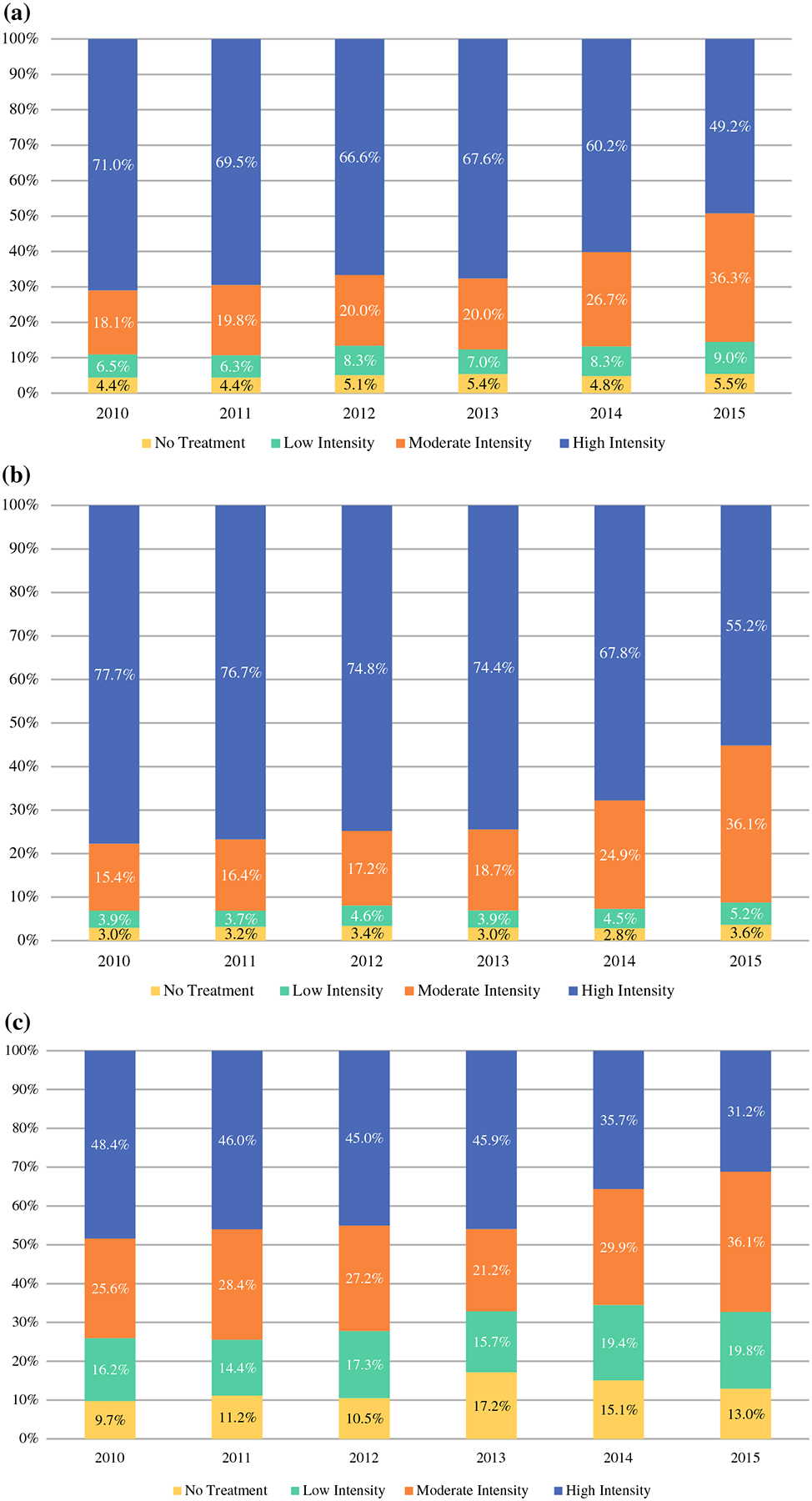
Locoregional therapy trends over time. a Locoregional therapy trends over time (whole cohort). Trends from 2010 to 2015 in women ≥ 70 years of age with T1N0 HR+ disease, by therapy intensity: high intensity: lumpectomy, axillary surgery and RT, or mastectomy and axillary surgery; moderate intensity: lumpectomy and RT, lumpectomy and axillary surgery, or mastectomy only; low intensity: lumpectomy only. b Locoregional therapy trends over time in non-frail women with a ≥ 5-year life expectancy. Trends from 2010 to 2015 in women ≥ 70 years of age with T1N0 HR+ disease who are robust and have a ≥ 5-year life expectancy, by therapy intensity: high intensity: lumpectomy, axillary surgery and RT, or mastectomy and axillary surgery; moderate intensity: lumpectomy and RT, lumpectomy and axillary surgery, or mastectomy only; low intensity: lumpectomy only. c Locoregional therapy trends over time in frail women with a < 50-year life expectancy. Trends from 2010 to 2015 in women ≥ 70 years of age with T1N0 HR+ disease who are frail and have a < 5-year life expectancy, by therapy intensity: high intensity: lumpectomy, axillary surgery and RT, or mastectomy and axillary surgery; moderate intensity: lumpectomy and RT, lumpectomy and axillary surgery, or mastectomy only; low intensity: lumpectomy only. HR+ hormone receptor-positive, RT radiation therapy
