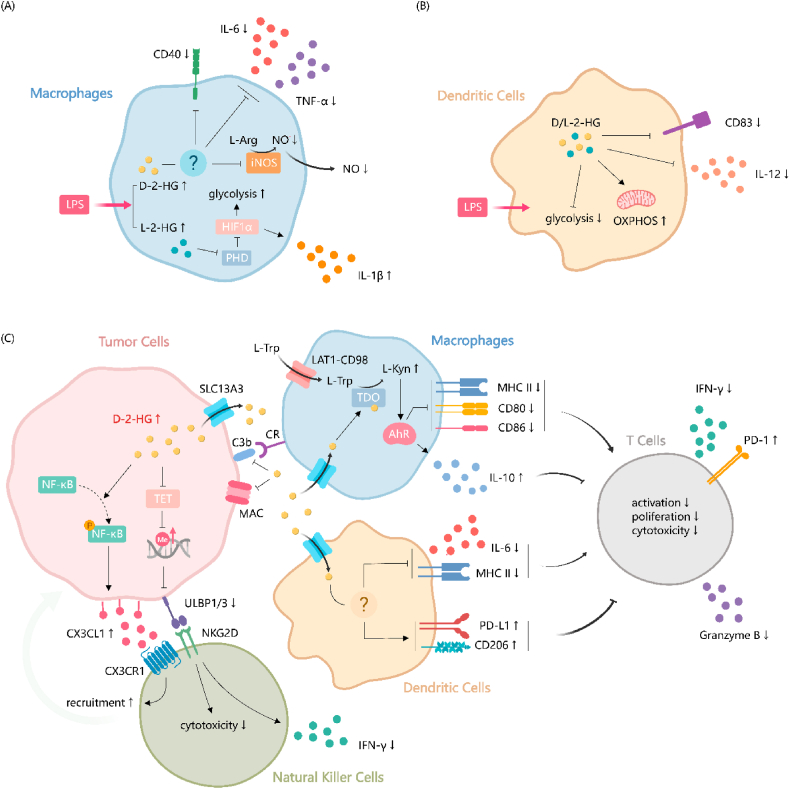
Fig. 3.
| Roles of 2-HG in modulating innate immune components. (A) LPS stimulation results in an increase of both D-2-HG and L-2-HG within macrophages. (B) Treatment with either D-2-HG or L-2-HG elicits a consistent response in LPS-activated DCs, characterized by diminished glycolysis, augmented OXPHOS, reduced secretion of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL12, and downregulation of the dendritic cell maturation marker CD83. (C) Within tumor cells, D-2-HG recruits NK cells through CX3CL1- CX3CR1 interaction. Concurrently, D-2-HG leads to a diminution in the cytotoxic capabilities and a decrease in IFN-γ production in NK cells by constraining the expression of NKG2D receptor ligands ULBP1/3. In tumor-associated macrophages, D-2-HG activates TDO/L-kyn/AhR and suppresses the expression of pro-inflammatory molecules such as MHCII, CD86, and CD80, while simultaneously upregulating the secretion of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL10. D-2-HG induces a tolerogenic phenotype in DCs. It upregulates the expression of immunosuppressive mediators such as PD-L1 and CD206 and reduces the expression of IL-6 and MHCII. Additionally, D-2-HG adversely impacts the complement system, characterized by less MAC formation and C3b deposition on tumor cell surfaces. Impaired the functions of macrophages and DCs indirectly inhibits T cell activity by. AhR, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; CR, complement receptor; CX3CL1, C-X3-C motif chemokine ligand 1; CX3CR1, C-X3-C motif chemokine receptor 1; D-2-HG, D-2-hydroxyglutarate; DC, dendritic cell; HIF1α, hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha; IFN-γ, interferon-gamma; IL-1β, interleukin-1 beta; IL-6, interleukin-6; IL-10; interleukin-10; IL-12, interleukin-12; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; L-kyn, l-kynurenine; L-trp, l-tryptophan; LAT1, L-type amino acid transporter 1; LPS, Lipopolysaccharide; MAC, membrane attack complex; MHCII, major histocompatibility complex class II; F-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; NK, natural killer; NKG2D, natural killer group 2D; NO, nitric oxide; OXPHOS, oxidative phosphorylation; PD-1, programmed death-1; PD-L1, programmed death-ligand 1; PHD, prolyl hydroxylase; SLC13A3, solute carrier family 13 member 3; TDO, tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase; TET, ten-eleven translocation; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha; ULBP1/3, UL16-binding protein 1/3.