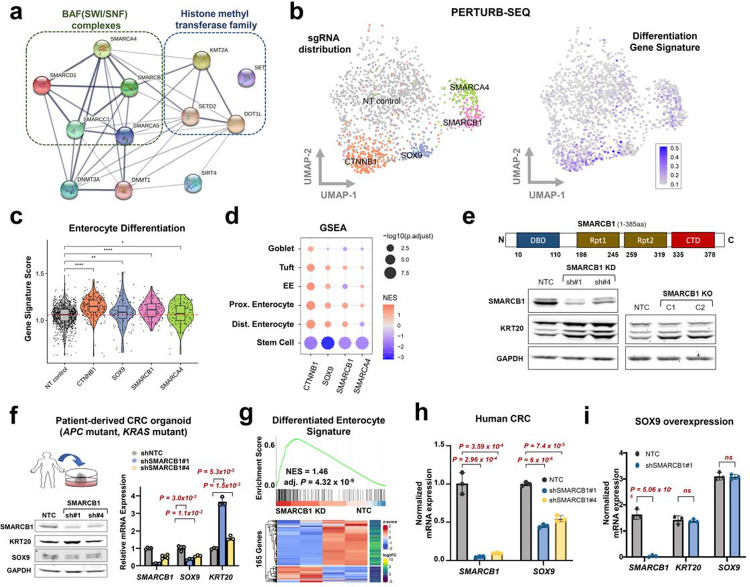
Figure 4. SMARCB1 restricts differentiation in models of CRC.
a. The gene and protein regulatory network among the genetic perturbations that promoted differentiation and impeded aberrant stem-cell activity in the dual reporter using STRING.
b. UMAP representation of CRISPR screening of select genes coupled with scRNA-seq readout (Perturb-seq). sgRNA assignment of each cell (left). Representation of intestinal differentiation gene signature (right) 79.
c. Violin plot depicting the enterocyte gene expression signature in cells with NT control, CTNNB1, SOX9, SMARCB1, and SMARCA4 sgRNAs.
d. GSEA of single cell transcriptomes from cells with CTNNB1, SOX9, SMARCB1, and SMARCA4 sgRNAs relative to NT controls using distinct differentiation and one stem cell signature (Haber et al., 2017).
e. Immunoblot of SMARCB1, KRT20, and GAPDH in HT-29 SMARCB1 KD cell lines using 2 shRNAs and HT-29 SMARCB1 KO clones using CRISPR-Cas9; C1 has 32.9% and C2 has 72.6% editing.
f. Immunoblot of SMARCB1 and KRT20 (left) and mRNA expression (right) of SMARCB1, SOX9, and KRT20 in the patient-derived CRC organoid transduced with 2 shRNAs against SMARCB1.
g. GSEA (top) and heatmap (bottom) of differentiation gene expression signature in bulk RNA-seq data from the patient-derived CRC organoid transduced with either NT Control or SMARCB1 KD shRNA.
h. mRNA expression of SMARCB1 and SOX9 in HT-29 SMARCB1 KD cell lines using 2 shRNAs.
i. mRNA expression of SMARCB1, KRT20, SOX9 in HT-115 control and SMARCB1 KD lines engineered to conditionally overexpress SOX9.