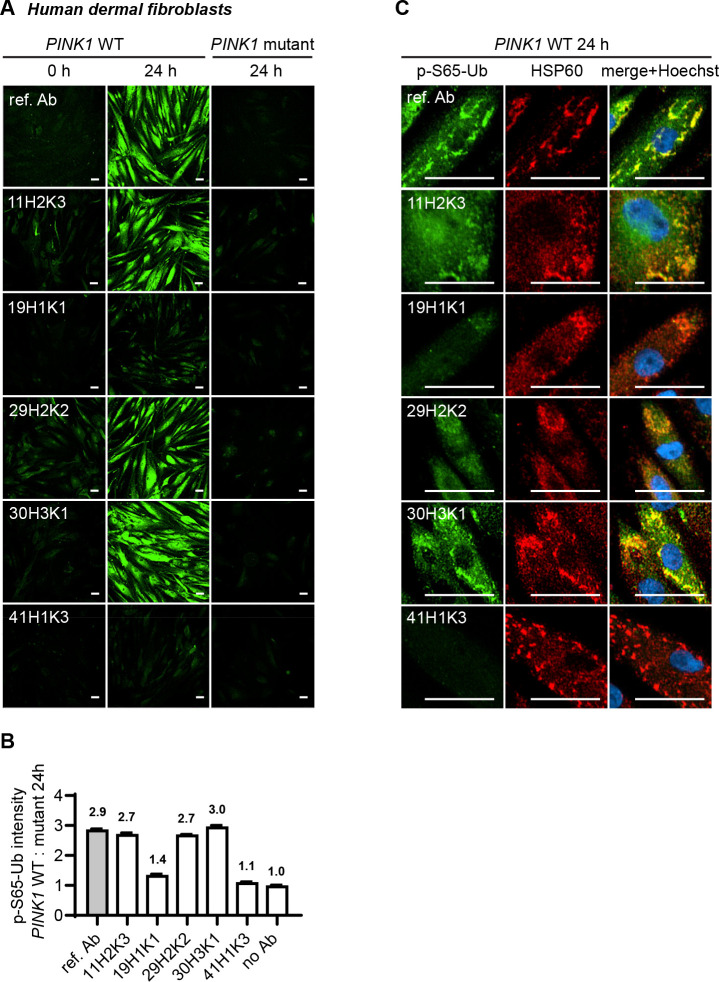
Figure 5.
Comparison of the top p-S65-Ub antibodies using immunocytochemistry staining of human dermal fibroblasts. All five p-S65-Ub recombinant antibodies and the reference antibody were evaluated by immunocytochemistry in human primary dermal fibroblasts treated with 2 μM valinomycin for 0 or 24 hours. All antibodies were used at 1 μg/ml. (A) Representative images of p-S65-Ub immunoreactive signals (green) in fibroblasts carrying WT or homozygous PINK1Q456X mutation. (B) Fluorescence intensities of each antibody was quantified by high content imaging and compared signals from treated WT to the signals from the corresponding PINK1 mutant fibroblasts. Fold changes are labeled at top of each bar. Samples stained without primary antibody was used a negative control (no Ab). N = 2. Data are shown as mean with SEM. (C) Representative zoom-in images of p-S65-Ub and HSP60 immunoreactive signals in treated WT fibroblasts. 24 hours of valinomycin treatment induced mitochondrial aggregation (HSP60, red) and the accumulation of p-S65-Ub (green). Nuclei were stained with Hoechst (blue). Scale bar: 50 μm. Ref. Ab - reference antibody, WT - wild-type.