Figure 1.
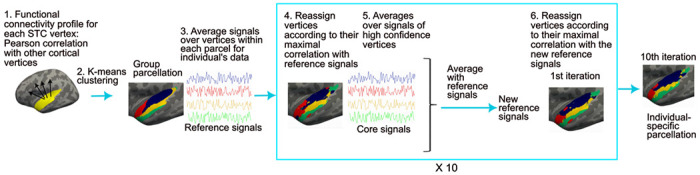
Individual-level functional parcellation method. 1) Pearson correlation was computed between the fMRI signal at each STC vertex and signals of all other cortical vertices in each participant. The individual-level connectivity profiles were averaged across participants at each vertex using a cortical surface-based atlas. 2) Group-level parcellation was computed by using K-means clustering, to cluster vertices with similar connectivity profiles into same network. 3) The individual participant’s fMRI signal time courses were then averaged across the vertices within each group-level network (reference signals). 4) The parcellation was adapted for each individual participant by reassigning vertices to networks according to their maximal correlation with the reference signals. For each vertex, a confidence value was computed as the ratio of the largest and second largest correlations. 5) For each new network of the adapted parcellation, an average was computed using the connectivity profiles of the vertices with confidence values larger than 1.3. The resulting “high-confidence signals” were averaged with the reference signals. 6) Using the resulting new reference signals, the STC vertices were further reassigned to one of the networks. Steps 4–6 were repeated ten times to generate an individual-specific parcellation.
