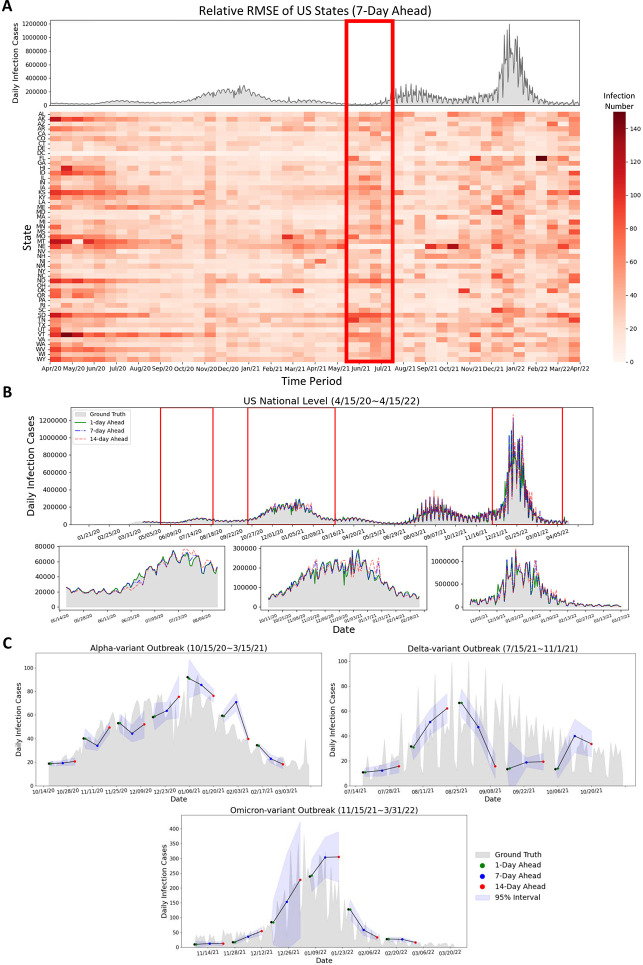
Figure 5:
Summary of forecasting results at the state and national level. (A) Relative RMSE performance among US states in the 7-day horizon at the state level is determined by the average relative RMSE of the last 7 days of each time period, compared to the national reported infection trend. The relative RMSE increased during the early period (April 2020 to May 2020) of the first upward trend, the time period (June 2021 to July 2021) before the Delta outbreak, and the increasing period (December 2021 to January 2022) of the Omicron COVID-19 outbreak. Missouri, Montana, and Nebraska have large relative RMSE values during March 2021 to May 2021. We can observe that the RRMSE errors often increase before the early stage of the next outbreaks or when the infection trend rapidly increases (red rectangle) (B) Daily prediction infection trends during different days ahead at the national level. It can be observed that the daily predicted infection trends at 1-day and 7-day ahead horizons show similarity to the reported data, while the 14-day ahead trend exhibits some fluctuations. (C) Daily predicted infection trends of the proposed model during Alpha-variant, Delta-variant, and Omicron-variant outbreaks with different days ahead predictions. The proposed FIGI-Net model can provide a curve of predicted trends matching the observed report. The range of margin of error became larger when the trend of Omicron-variant outbreak increased.