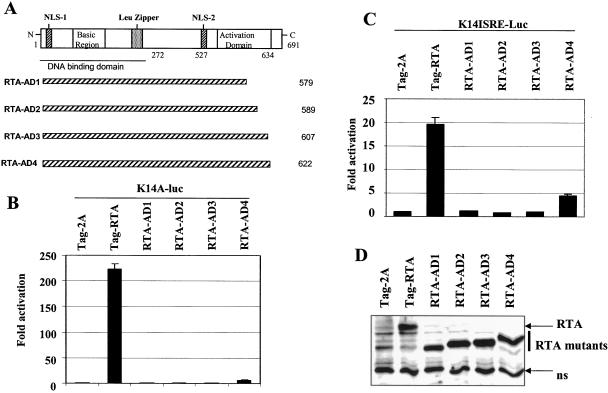
FIG. 2.
The activation domain of RTA is required for activation of the K14-ORF74 promoter. A. Schematic diagram of RTA domains and mutants. The number of amino acid residues is shown. The basic region of the RTA and leucine zipper regions, activation domain, DNA-binding domain, and nuclear localization signal (NLS) are shown. B. The activation domain of RTA is required for activation of the K14-ORF74 promoter. 293T cells were transfected with reporter construct, K14A-luc, along with CMV-β-Gal and equal amounts (50 ng) of RTA or various mutant expression plasmids. The relative reporter activity is shown. C. The activation domain of RTA is required for activation of the K14 ISRE. 293T cells were transfected with reporter construct, K14ISRE-luc along with CMV-β-Gal, and equal amounts (0.3 μg) of RTA or various mutant expression plasmids. The reporter activity is expressed relative to the vector control. Luciferase activity was normalized by β-galactosidase activity. Standard deviations are shown. D. Expression status of RTA and its deletion mutants. Western blotting with Flag monoclonal antibody was performed. The cell lysates from transfected cells are indicated. The identity of proteins is as shown. ns, nonspecific.