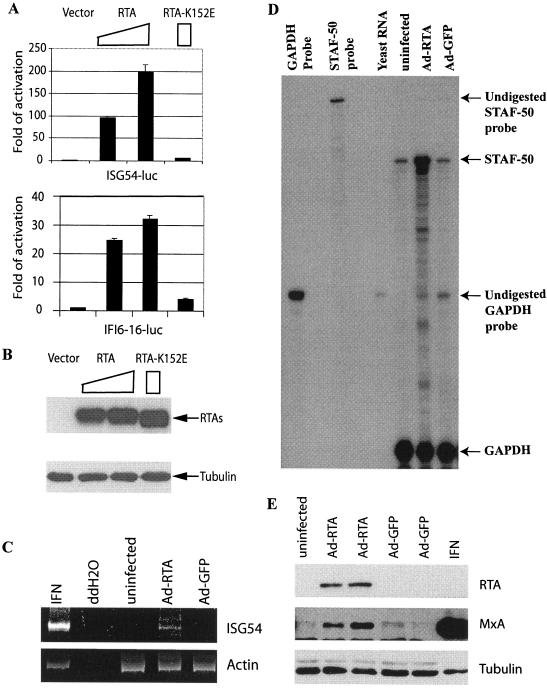
FIG. 7.
RTA selectively induces the expression of IFN-stimulated genes. A. RTA activates IFN-inducible promoter reporter constructs. ISG54-luc or IFI6-16-luc promoter constructs were transfected into 293T cells along with various amounts of RTA expression plasmids (0.1 or 0.3 μg) or with RTA K152E expression plasmid (0.3 μg). Luciferase activity was normalized by β-galactosidase activity. The relative reporter activities are shown with standard deviations. B. Expression levels of RTA mutants. Western blot assays with RTA as well as tubulin antibodies were performed. The cell lysates from transfected cells are indicated. The identities of proteins are shown. C. RTA induces ISG-54 in HUVECs. RNAs from uninfected HUVECs or the cells infected with recombinant adenovirus with RTA or GFP, respectively, were used for RT-PCR analyses. IFN-α (100 IU/ml)-treated 293 cells were used as a positive control. D. RTA induces STAF-50 in HUVECs. STAF-50 and GAPDH probes were labeled with [α-32P]UTP and used for RPA. Specific protections of STAF-50 and GAPDH mRNAs and undigested probes are indicated. Relative STAF-50 RNA levels (STAF-50/GAPDH) were increased 5.3 ± 0.9-fold. The data were obtained by normalizing STAF-50 to GAPDH levels from three independent experiments with the use of a Gene Genius Bioimaging system. E. RTA induces the expression of MxA protein. Lysates from uninfected, AdRTA-infected, AdGFP-infected, or IFN-α (100 IU/ml)-treated HUVECs were used for Western blot analysis. The same membrane was stripped and reprobed with other antibodies. The identities of proteins are shown.