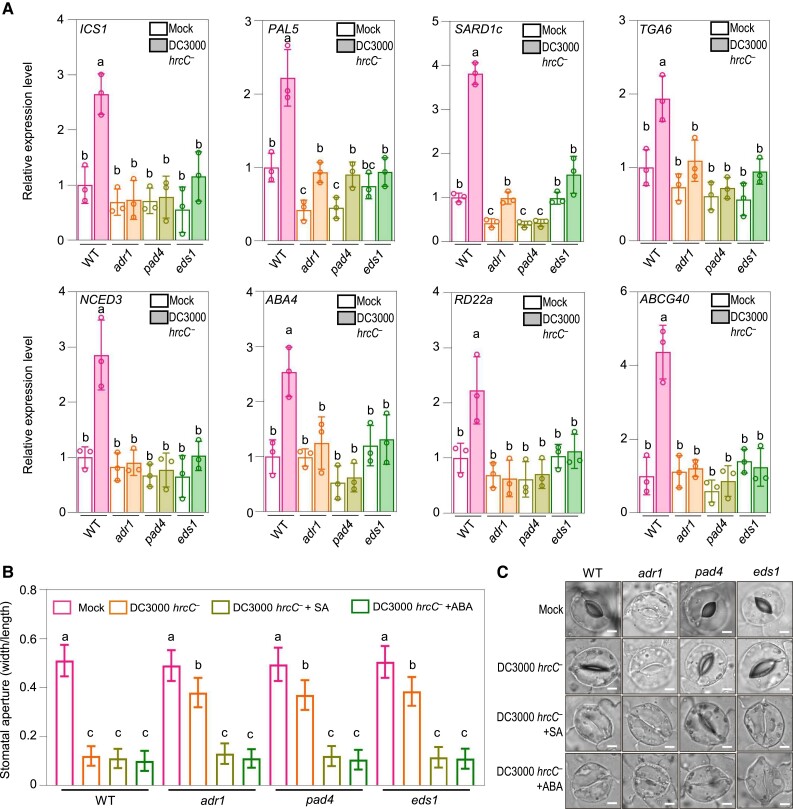
Figure 4.
NbADR1, NbEDS1, and NbPAD4 function upstream of SA and ABA pathways in stomatal closure. A) Quantitative reverse transcription PCR analysis of the representative SA pathway genes ICS1, PAL5, SARD1c, and TGA6, and the representative ABA pathway genes NCED3, ABA4, RD22a and ABCG40 in Nicotiana benthamiana wild-type (WT), adr1, pad4, and eds1 at 2 h postspray inoculation with mock (10 mM MgCl2) or Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato (Pst) DC3000 hrcC− (OD600 = 0.4). Data are means (±Sd) of 3 biological replicates from independent plants. Letters indicate significant differences by 1-way ANOVA analysis (Tukey's post hoc test, P < 0.05). B, C) Stomatal apertures B) and images of stomata C) in leaves of N. benthamiana WT and the indicated mutants after 1 h of flood treatment with mock (10 mM MgCl2), Pst DC3000 hrcC− (OD600 = 0.4), or Pst DC3000 hrcC−(OD600 = 0.4) plus SA (the form of sodium salicylate) or ABA, respectively. Data are means ± Sd; n = 50 stomata. Letters indicate significant differences by 1-way ANOVA analysis (Tukey's post hoc test, P < 0.05). Scale bars represent 5 μm. The experiments were repeated 3 times with similar results.