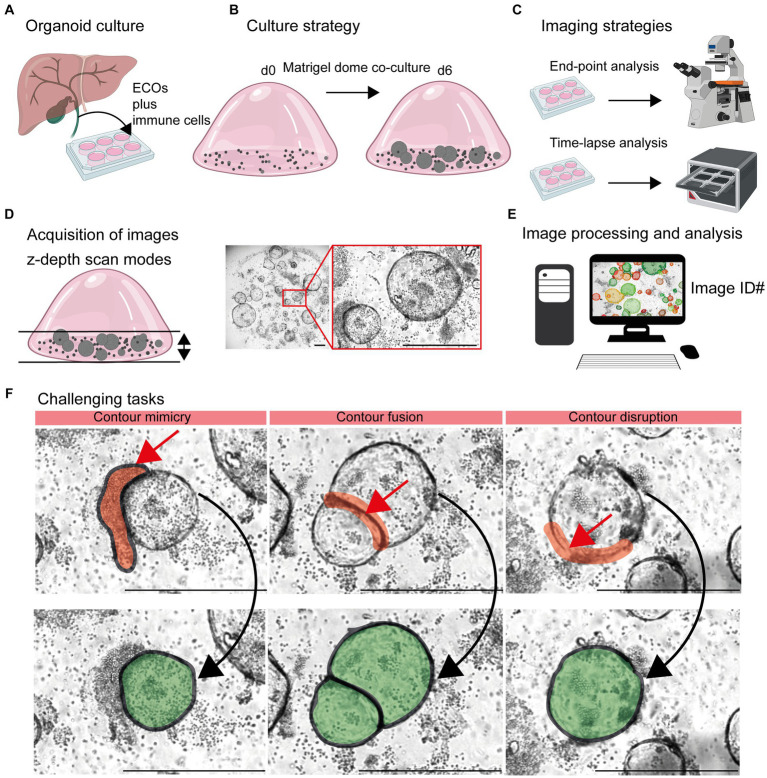
Figure 1.
Detection of organoids in co-cultures of organoids and immune cells. (A) Organoid culture: Extrahepatic cholangiocyte organoids (ECOs) were generated from gallbladder tissue. (B) Culture strategy: ECOs and immune cells embedded in Matrigel® were co-cultured for a period of 6 days. Details are given in Section 2.2 and 2.3. (C) Imaging strategies: Culture plates are incubated within cell incubators for end-point analysis or the Incucyte® system, allowing an incubation and imaging for a period of 6 days. (D) Acquisition of images: Capturing red, green and blue (RGB) images with z-depth enables the generation of images with high plasticity. (E) Image processing and analysis: Import of images and image identification information (ID: well number and time point) in suitable devices for subsequent detection and quantification of organoids by the StrataQuest-supported Organoid App. (F) Challenging tasks: The main challenging tasks of organoid detection are depicted. Upper row: Red arrows indicate contour mimicry (left), contour fusing (middle) or contour disruption (right). Red areas highlight the regions that might interfere with a precise detection of organoids. Lower row: The aimed precision of organoid detection is highlighted in green. The bars represent 500 μm.