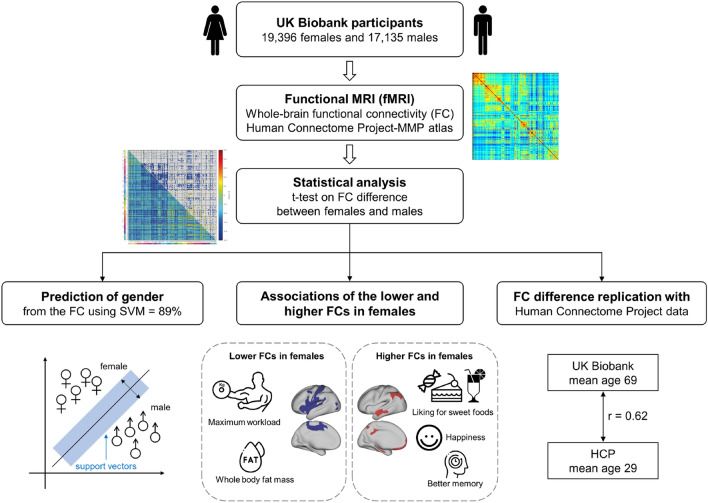
Fig. 1.
Workflow and summary of findings. Functional connectivity was calculated, and differences for females minus males were calculated with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons. Association analyses with measures in the UK Biobank showed that many of the lower functional connectivities in females were for somatosensory/motor cortical regions, and were correlated with lower maximal workload and higher body fat mass. The higher functional connectivities in females were correlated with higher liking for sweet food, happiness, and better memory scores