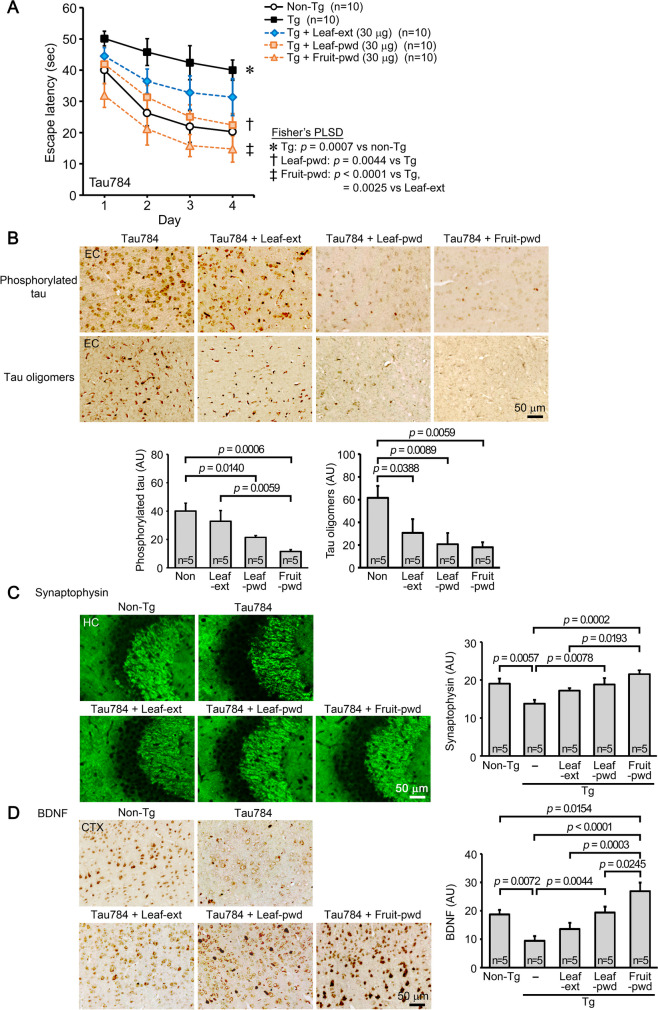
Fig. 5.
Comparison of hot water extract and non-extracted simple crush powders of Mamaki leaves and fruits in Tau784 mice. Hot water extract of Mamaki leaves (Leaf-ext), simple crush powder of the leaves (Leaf-pwd), and simple crush powder of the fruits (Fruit-pwd) were orally administered to 7–9-month-old Tau784 mice (mean body weight, 28.9 g) at 30 μg/day for 1 month. A Leaf-ext improved mouse memory incompletely, while Leaf-pwd significantly improved it to a level similar to that of non-Tg littermates. Fruit-pwd markedly enhanced mouse memory to a level even higher than that of non-Tg littermates. B The levels of phosphorylated tau in the entorhinal cortex (EC) were significantly decreased by Leaf-pwd and Fruit-pwd, with Fruit-pwd showing the strongest effect. Leaf-ext showed only slight effects. The levels of tau oligomers were significantly reduced by all preparations, with Fruit-pwd showing the highest effect and Leaf-ext the lowest. C The levels of synaptophysin in the hippocampal CA2/3 regions were significantly recovered by Leaf-pwd and Fruit-pwd, with Fruit-pwd showing the strongest effect. Leaf-ext restored synaptophysin levels only incompletely. D The levels of BDNF in the cerebral cortex (CTX) were significantly increased by Fruit-pwd to a level even higher than that in non-Tg littermates and also by Leaf-pwd but to a level similar to that in non-Tg littermates. Only slight effects were observed with Leaf-ext