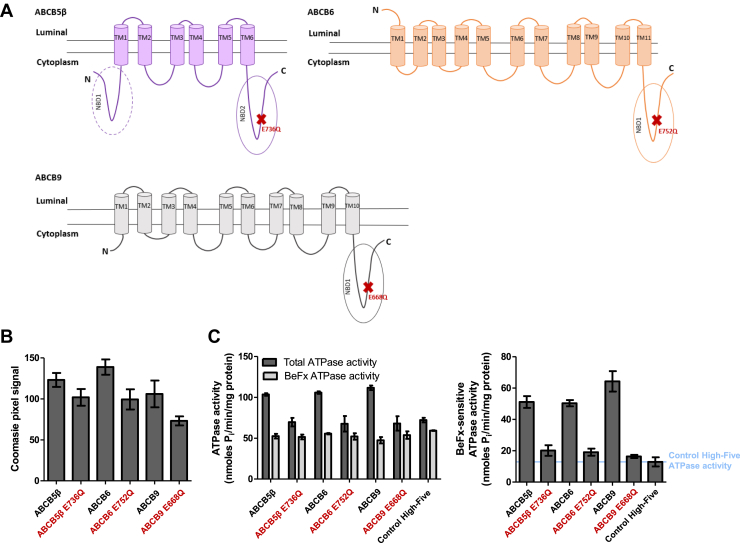
Figure 6.
Expression of homodimers in High-Five cells and BeFx-sensitive ATPase activity.A, two-dimensional schematic representation of ABCB5β (purple), ABCB6 (orange), and ABCB9 (gray) structure based on CCTOP predictions (61). ABCB5β has one complete and another partial NBD and one TMD comprised of six transmembrane helices (TMs). The N-terminal NBD (NBD1) is truncated and lacks the conserved Walker A domain. ABCB6 has six transmembrane helices (TM6-TM11) that constitute its TMD1 and five additional transmembrane helices (TM1-TM5) in the N terminus that form the TMD0. ABCB9 has a TMD1 consisting of six transmembrane helices (TM5-10) and a TMD0 made of four transmembrane helices at the N terminus. The location of each EQ mutation is represented by red Xs. B, pixel intensity quantification of the protein bands of interest, after Coomassie-blue staining was performed using ImageJ (n = 3). C, ABCB5β, ABCB6, ABCB9, and their corresponding EQ mutants’ ATPase activities were measured in the presence and absence of BeFx as described in the methods section. On the left, data are shown as ATPase activity in the absence of BeFx (total ATPase activity) and in the presence of BeFx (BeFx-sensitive ATPase activity). On the right, data are represented by subtracting BeFx-resistant ATPase activity from the total ATPase activity (n = 3). In all panels, the names of EQ mutants are shown in red. NBD, nucleotide-binding domain; BeFx, beryllium fluoride.