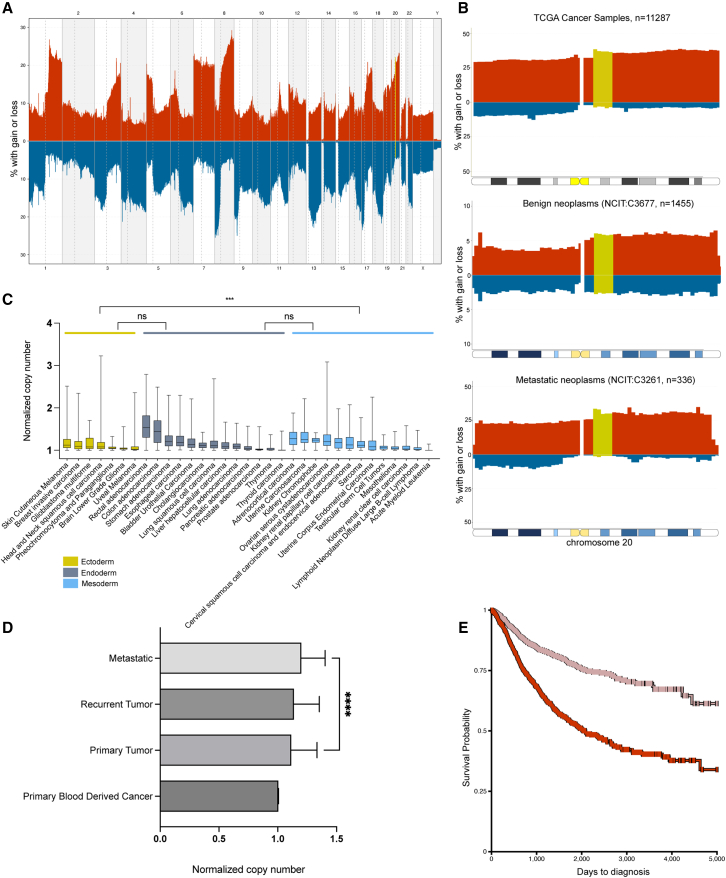
Figure 2.
Copy-number alterations of human chromosome 20q11.21 in cancers
(A) Aggregated copy-number variation (CNV) data of 117,587 neoplasms (NCIT: C3262) from the Progenetix database (Huang et al., 2021) were plotted using R library pgxRpi. The percentage of samples with aberrations (red, gain; blue, loss) for the whole chromosome are indicated on the y axis. Chromosomal regions are depicted on the x axis; the minimal region of interest at chr20:31216079-35871578 is marked in moss green. NCIT, National Cancer Institute Thesaurus.
(B) Top to bottom: Aggregated CNV data of 11,287 TCGA cancer samples, 336 metastatic neoplasms (NCIT: C3261), and 1,455 benign neoplasms (NCIT: C3677) from the Progenetix database (Huang et al., 2021), respectively, were plotted using R library pgxRpi. The percentage of samples with aberrations (red, gain; blue, loss) for the whole chromosome are indicated on the y axis. Chromosomal regions are depicted on the x axis; the minimal region of interest at chr20:31216079–35871578 is marked in moss green.
(C) Amplification of chromosome 20q11.21 (31216079–35871578) found across various tumor types categorized according to the germ layer to which the cell of origin of the tumor belongs. Box and whiskers plot for normalized copy-number gain (tumor/normal) of chromosome 20q11.21 (31216079–35871578) in respective cancers as indicated. The box extends from the 25th to the 75th percentile, whiskers indicate the smalles and largest values, the median is indicated as a line in the box. Data extracted from TCGA-PANCAN database using the University of California, Santa Cruz (UCSC) Xena online platform (Goldman et al., 2020), skin cutaneous melanoma (n = 403), breast invasive carcinoma (n = 848), glioblastoma multiforme (n = 535), head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (n = 414), pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma (n = 154), brain lower-grade glioma (n = 451), uveal melanoma (n = 52), rectal adenocarcinoma (n = 150), colon adenocarcinoma (n = 367), bladder urothelial carcinoma (n = 358), cholangiocarcinoma (n = 29), esophageal carcinoma (n = 160), liver hepatocellular carcinoma (n = 278), lung adenocarcinoma (n = 360), lung squamous cell carcinoma (n = 430), pancreatic adenocarcinoma (n = 154), prostate adenocarcinoma (n = 419), stomach adenocarcinoma (n = 338), thymoma (n = 53), thyroid carcinoma (n = 342), adrenocortical carcinoma (n = 74), cervical squamous cell carcinoma and endocervical adenocarcinoma (n = 228), lymphoid neoplasm diffuse large B cell lymphoma (n = 24), kidney chromophobe (n = 60), kidney renal clear cell carcinoma (n = 417), kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma (n = 168), AML (n = 107), mesothelioma (n = 73), ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma (n = 521), sarcoma (n = 199), testicular germ cell tumors (n = 97), uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma (n = 297), and uterine carcinosarcoma (n = 50). The Dunn’s test p value is indicated between groups of 3 germ layers: ectoderm (n = 2,857), yellow; endoderm (n = 3,438), gray; and mesoderm (n = 2,315), blue; ns, not significant; ∗∗∗ p=0.0006. Significant differences in amplifications were found across various tumor types within groups, ectoderm (Kruskal-Wallis test, p < 0.0001), endoderm (Kruskal-Wallis test, p < 0.0001), and mesoderm (Kruskal-Wallis test, p < 0.0001), not indicated in the figure."
(D) 20q11.21 has a significantly increased copy number in metastatic samples. Normalized copy numbers (tumor/normal) are depicted on the x axis (median with interquartile range) for primary blood-derived cancers (n = 118); primary tumor (n = 8,610), recurrent tumor (n = 53) and metastatic (n = 332) samples. Copy number of metastatic samples is significantly higher compared to the primary tumors (Mann-Whitney U test, p < 0.0001). No significant difference was observed between primary tumor and recurrent tumors (Mann-Whitney U test, p = 0.8441). Data were extracted from TCGA database using the UCSC Xena online platform (Goldman et al., 2020).
(E) Patients carrying amplifications of 20q11.21 have poor disease-specific survival. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis curve for patients carrying balanced (log[tumor/normal] < 0.03600, n = 1,993, pink) and amplified (log[tumor/normal] > 0.3054, n = 1,932, red) loci, p = 0.00. Primary tumors carrying aberration values of log(tumor/normal) ≥ 0 at 20q11.21 (31216079–35871578) loci were used to select for samples. Kaplan-Meier curve was made using the UCSC Xena online platform (Goldman et al., 2020). The x axis depicts time in days to diagnosis and the y axis depicts probability of survival. Source data for the entire figure can be found in Table S2.