Figure 10. Illustration of the key findings and hypotheses of the AAT–GR interactions.
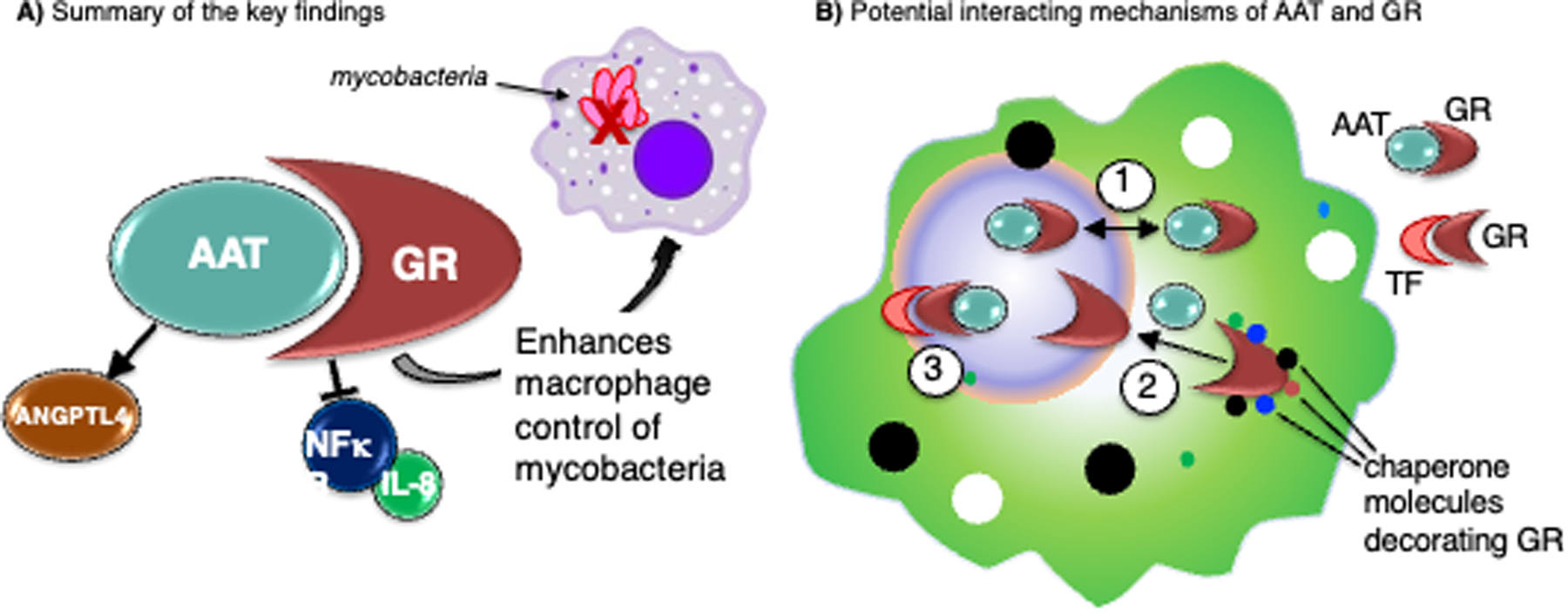
(A) Summarizing the key findings, alpha-1-antitrypsin–glucocorticoid receptor (AAT–GR) interaction inhibits nuclear factor-kappa B (NFκB) activation and interleukin-8 (IL-8) production, induces angiopoietin-like 4 (ANGPTL4), and enhances macrophage control of mycobacteria. (B) Several hypotheses of how AAT–GR interaction may affect cellular function: (1) AAT may shuttle GR between the nuclear and cytoplasmic compartments; (2) AAT may facilitate disassembly of GR–chaperone complexes; (3) AAT may stabilize transcriptional complexes of GR–transcription factor (TF, orange structure) or locally modulate the activity of proteases.
