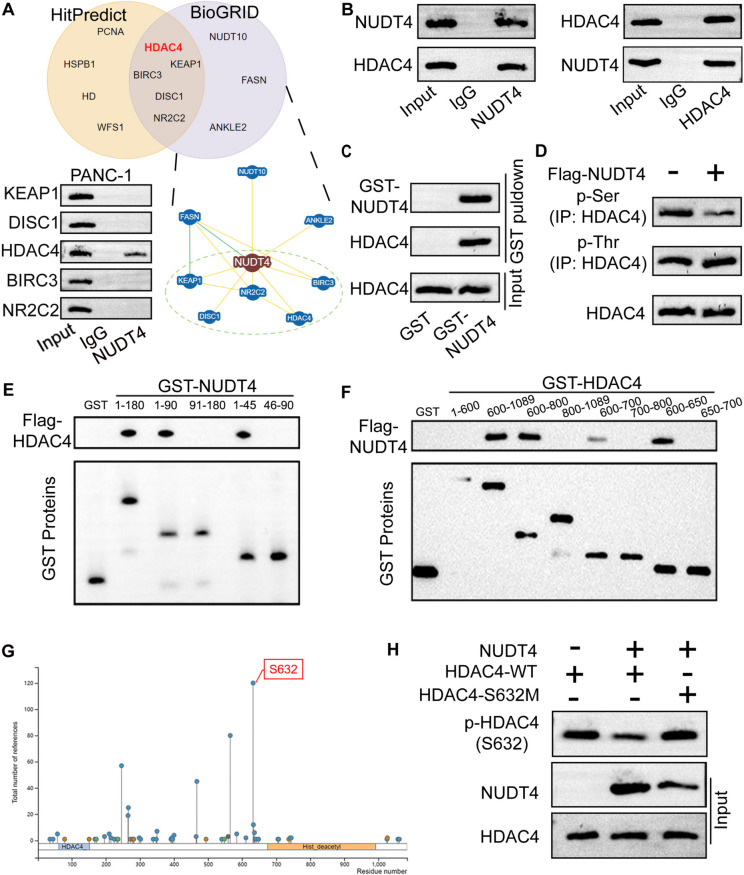
Fig. 4.
NUDT4 regulates dephosphorylation of HDAC4 protein. A The online HitPredict and BioGRID bioinformatic tools were used to predict candidate NUDT4-interacting proteins, and candidate proteins identified with both tools were screened using Co-IP assays. B, C GST pulldown and Co-IP assays confirmed the physical interaction between NUDT4 and HDAC4 in 293 T cells. Anti-lgG and anti-NUDT4 antibodies were used in the Co-IP experiments (B), and GST-NUDT4 was used for the GST pulldown assay (C). D IP-WB assays illustrated that NUDT4 inhibited serine phosphorylation (p-Ser) rather than threonine phosphorylation (p-Thr) on HDAC4. E, F GST pulldown assays were performed to analyze the binding of NUDT4 fragments (aa 1–180, 1–90, 91–180, 1–45, or 46–90) with HDAC4 fragments (aa 1–600, 600–1089, 600–800, 800–1089, 600–700, 700–800, 600–650, or 650–700) in 293 T cells, which showed that aa 1–45 of NUDT4 interacted with aa 600–650 of HDAC4. G PhosphoSitePlus online stool was used to predict the phosphorylation sites of HDAC4. H IP-WB experiments indicated that NUDT4 could dephosphorylate WT HDAC4 at S632, and this dephosphorylation was hindered when S632 was mutated (HDAC4-S632M)