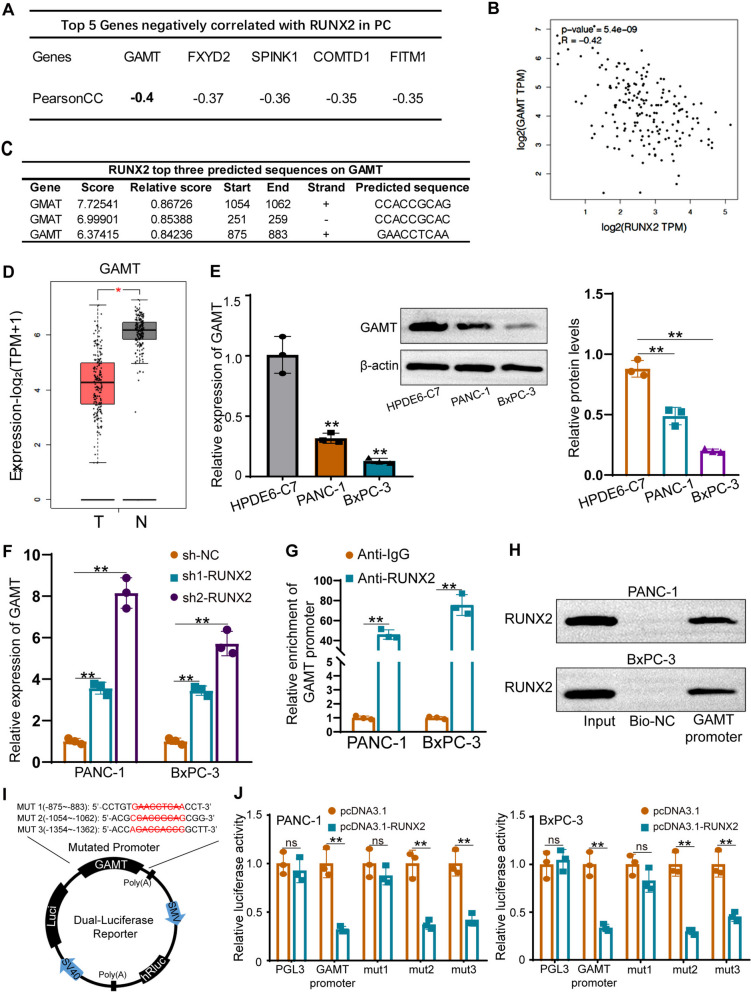
Fig. 7.
RUNX2 transcriptionally inhibits GAMT expression. A The online UALCAN tool was used to predict genes that correlate negatively with RUNX2 expression in PC cells, based on TCGA data. Candidate downstream genes and Pearson correlation coefficients (PearsonCC) are shown. B The GEPIA database was used to predict GAMT and RUNX2 co-expression in PC cells. A non-log scale was used for calculations, a log-scale axis was used for visualization, and Spearman’s correlation coefficient was determined. C JASPAR database analysis revealed potential RUNX2-binding sites in the GAMT promoter region. The top three predicted binding sites are shown. D GAMT expression in PC tissues and normal tissues was studied using the GEPIA database. GAMT expression level was defined by log2(TPM + 1), number of pancreatic tumor tissues (T) = 179, number of normal pancreatic tissues (N) = 171. E GAMT mRNA and protein expression levels in PANC-1 and BxPC-3 cells were detected using qRT-PCR and WB analysis, respectively. F qRT-PCR analysis of GAMT expression in BxPC-3 and PANC-1 cells when RUNX2 was silenced. G, H ChIP and DNA pulldown assays were used to verify the interaction between RUNX2 and the GAMT promoter. I Schematic diagram of the luciferase reporter plasmids with three mutated GAMT promoter sequences (MUT1-MUT3). J WT and mutated GAMT promoters were used in dual-luciferase reporter assays. ns: no significance, **p < 0.01