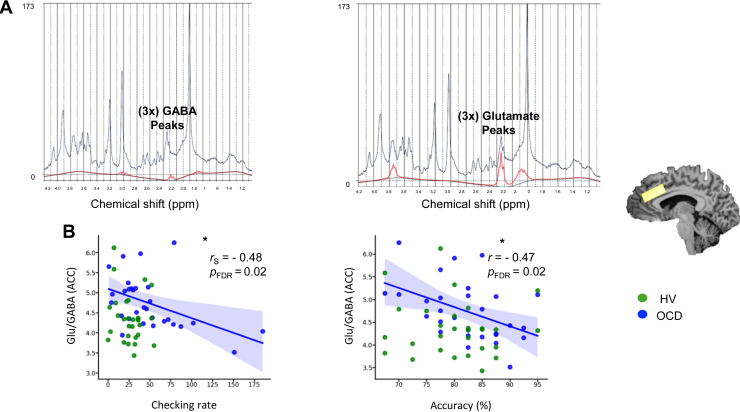
Figure 5.
Relationship between image verification task checking rates and brain neurochemical measurements. (A) Examples of the LCModel analysis of in vivo 1H magnetic resonance spectra acquired from a healthy volunteer (HV) at 7T (semi-LASER, echo time/repetition time = 1.99/4300 ms, from a 20 × 20 × 20 mm3 voxel placed bilaterally at the anterior cingulate cortex [ACC]). The acquired spectrum is plotted in black, and the fit is presented in red for GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) (left) and glutamate (Glu) (right). (B) The correlations between the levels of Glu/GABA concentrations in the ACC and checking rates (left) and accuracy (right). The blue color represents patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) (N = 30), whereas green depicts the data for HVs (N = 29). The fitted lines are drawn only for significant relationships in the OCD group, with the 95% CIs for the regression estimate in translucent bands around the regression lines. The neurometabolites were normalized using (Cr+PCr), corrected for gray and white matter and cerebrospinal fluid of each individual voxel, within participants. r indicates Pearson correlation coefficient, and rS indicates Spearman rank correlation coefficient. ∗p < .05. FDR, false discovery rate; ppm, parts per million.